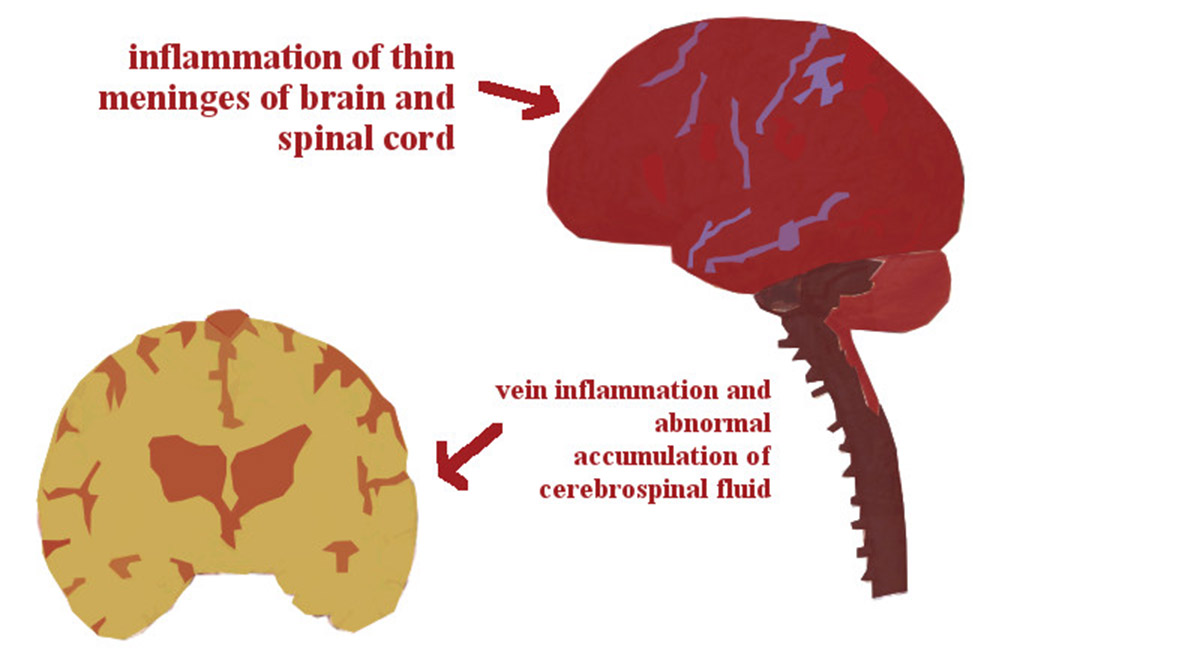
Meningitis is an inflammation of the brain or brain tissue that surrounds the brain. Meningitis can be caused by the viral or bacterial infection. Viral meningitis is more common and less dangerous than bacterial meningitis.
Viral meningitis mainly occurs in children older than 5. Bacterial meningitis is rare but life-threatening. The types of bacterial meningitis are group A, B and C meningococcus bacteria. The best known is the group B meningococcus bacteria. It can appear at any age, but still it is the most common in children under age of 5.
The symptoms of meningitis
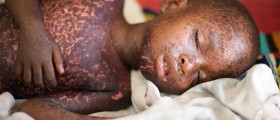
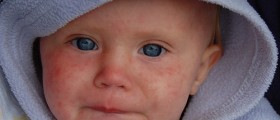
Early symptoms of bacterial meningitis are similar to flu symptoms, but symptoms of bacterial meningitis are usually much stronger. The greatest risk of bacterial meningitis is that it develops very quickly, so the child becomes seriously ill for a few hours, feeling sleepy or even loses consciousness. Cramps also often appear.Some children who become ill from meningitis get characteristic rash consisted of tiny dots of blood under the skin. A rash can occur anywhere on the body. Spots are flat, pink or purple. In the first stage they look like injected spots, but if aren’t treated, they grow and eventually look like bruises.
Besides this, the symptoms also include: fever with cold hands and feet, stiff neck nervousness, restlessness, headaches and intolerance to strong light and noise. If there are any of these symptoms, child should be taken to the doctor.
Complications
If isn’t started with adequate treatment on time, in children can be developed scars as witnesses of infection. These scars usually impede the normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid, forming obstacles which cause accumulating of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain and leads to pressure on the brain structure. Increased pressure inside the skull causes the deterioration of brain cells and leads to the displacement and suppression of parts of the brain which can have fatal consequences such as hydrocephalus.Encephalitis can also occur if with adequate treatment is late.
Above mentioned can decrease the intellectual abilities of the child and lead to mental retardation. Fortunately, in most children in whom the diagnosis turns out on time, and starts the right treatment these complications not happen.
Treatment
Bacterial meningitis falls in urgent situations. Patients must be hospitalized and subjected to treatment with intravenous antibiotics. A doctor can determine the antibiotic treatment to anyone who was in contact with the sick child in order to prevent the spread of disease.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...