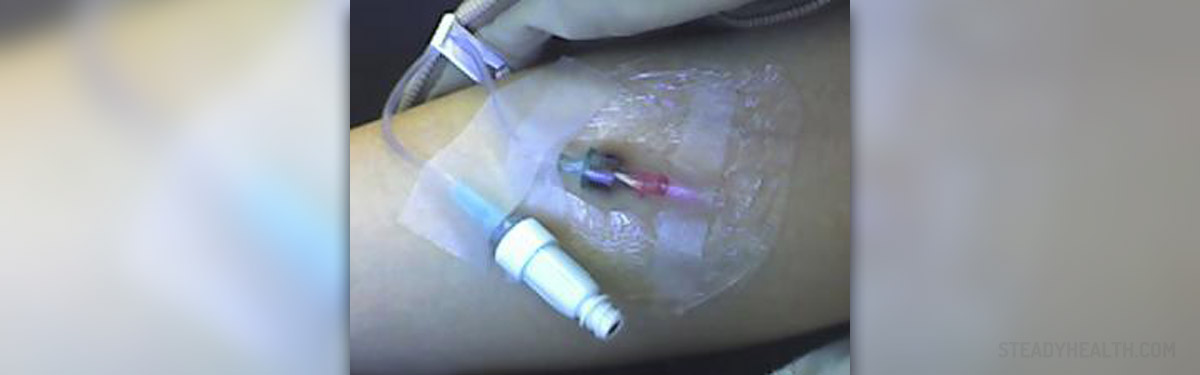
Intravenous Therapy
Intravenous therapy, or IV therapy for short, refers to the practice of administering fluids directly into the vein. Intravenous therapies are known as specialty pharmaceuticals. The intravenous route of administering and distributing fluids and medications is the fastest one compared to other methods, and it is done when quick action is needed.
Risks of Intravenous Therapy
There are numerous risks associated to intravenous therapy such as infection, phlebitis, infiltration, fluid overload, electrolyte imbalance, embolism, and extravasation. These risks will be low if the IV therapy is administered by a fully-trained and experienced professional, but it is good to be aware of them.
Infection
Even though intravenous therapy is an antiseptic procedure, infection may occur due to Coagulase-negative staphylococcus or Candida albicans entering through injection site. Also, bacteria may be accidentally introduced from contaminated equipment. Usually, these infections are local and include swelling and redness around injection site and fever. If bacteria enter the blood stream it may cause the potentially lethal infection septicemia.
Phlebitis
Phlebitis represents inflammation of a vein due to infection, IV catheter, or administered liquids. Symptoms of phlebitis include swelling, pain and redness around the vein. Veins can become sclerotic and hard to access because of repeated injections and recurring phlebitis.
Infiltration
Infiltration takes place if intravenous fluid enters nearby tissue instead of the vein. Symptoms of infiltration are local swelling or edema and the skin paleness. This side effect of IV therapy isn’t serious and it is treated by removing the needle and elevating the affected limb in order to drain the accumulated fluids.
Fluid Overload
Fluid overload happens if fluids are administered at higher rate or in a larger volume than the system can take in or expel. This can lead to numerous complications, including hypertension, heart failure, and pulmonary edema.
Electrolyte Imbalance
An electrolyte imbalance can occur during IV therapy because of a too diluted or too concentrated solution.
Embolism
Embolism represents an air bubble or blood clot brought into circulation through an IV line, which can eventually block a vessel. Central IV carries higher risk of embolism.
Extravasation
Extravasation occurs in case of leakage of drugs into the surrounding tissue, after which infiltrated medication is damaging the tissue. This happens more frequently during chemotherapy and in people suffering from tuberculosis.
Complications of IV Therapy
Complications can be connected to a catheter when it is accidentally removed from the vein thus allowing drugs and fluids to enter nearby tissue (infiltration or extravasation). Also, during insertion of central catheter, the lung may be nicked which will allow air to leak from the lungs into the chest cavity.
An allergic reaction may always occur because of given medications, which is why doctors always ask patients if they are known to be allergic to any medications. If electrolyte solutions are administered too rapidly it may result in heart rhythm abnormality. Circulatory overload can occur if too high a fluid volume is injected, a situation that competent and experienced health care providers will know to avoid. In blood transfusion, complications may happen if there are incompatibilities of blood type.
If you notice any unusual symptoms following IV therapy, always let your health care provider know right away!








_f_280x120.jpg)



Your thoughts on this
Loading...