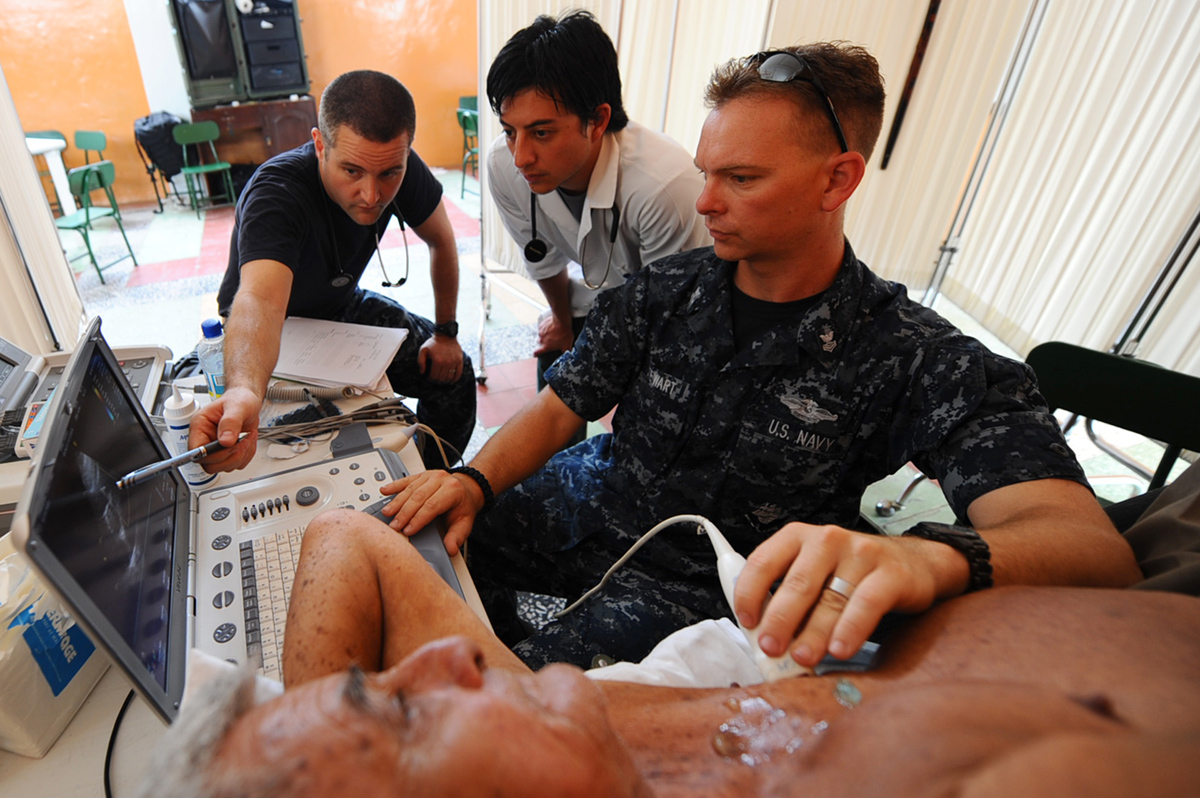
One of the ways in which it is possible for people with fast heart rhythm to have normal heart beats again is a procedure called cardioversion. In the greatest majority of the cases this medical procedure is done in a way which requires electrodes to be positioned on the patient’s chest and through them electric shocks have to be sent right to the heart. Before this procedure, the patient has to be sedated. On the other side, there is a possibility to perform cardioversion by the use of medicines but this is a very rarely chosen method. As we can see, this is not a surgery procedure, but it is very effective for a number of patients. One more advantage is related to the fact that although it has to be done in the hospital the patient can go home the same day. It is important for a patient who is thinking about undergoing this kind of the procedure to be aware of the fact that only certain problems with heart rhythm can be corrected while this method cannot be used in the cases of fibrillation (irregular heartbeat) and tachycardia (too fast heartbeat). It is also important for a patient to be well informed and to know what to expect during the procedure.
Risks and Complications
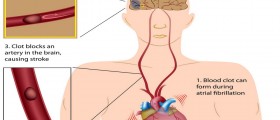
Some risks and complications are possible, even though this procedure is considered to be very safe in general. Its safety is implied by the fact that even pregnant women can undergo cardioversion. However, in order to avoid any possible complications, it is necessary to check whether or not the patient has blood clots somewhere in the heart, and to prescribe adequate medicines that will destroy blood clots, in case there are some. Otherwise, electric cardioversion might provoke the movement of these blood clots from one part of the body to another, thus putting the patient at risk of a stroke or pulmonary embolism if the clot gets to the heart or the lungs, for example. The outcome in such a situation may even be fatal. Another possible complication is actually a new problem related to the heart rhythm that a patient might develop after cardioversion. In such cases, though they are rare, the doctor will have to decide whether additional electric shocks are necessary, or the new problem can be handled by medications. One more occurrence that is possible after electric cardioversion is a problem with skin burns. However this happens even rarer than any other complication, so it should not pose a threat to a patient. Such burns usually appear on the places on which the electrodes were positioned.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...