Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone or bone marrow, usually caused by (pyogenic bacteria or mycobacteria. Pyogenic bacteria are those that are associated with infections that make puss. Mycobacterium is a genus of Actinobacteria, known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis and leprosy. Infection of the bone usually occurs when these microorganisms reach the bone through the bloodstream or as a result of penetrating trauma. When the bone is infected, white blood cells rush to the infection site, releasing the enzymes that lyse the bone. Lysis is a process in which the cells break down and the integrity of bone is compromised. Devitalized bone forms a foundation for chronic infection. Sometimes, the body tries to substitute for this loss and create a new bone around the place where death of cells and living tissue occurred.
Chronic osteomyelitis causes
Chronic osteomyelitis usually results from the presence of bacteria inside the bone cells. These bacteria can migrate from the infection site and invade other bone cells, leading to further loss of the bone. In some cases, bacteria become resistant to antibiotics, which lead to difficulties in eradication of this disease.
The most common causes are different in various age groups. Streptococcus aureus, Enterobacter species, and group A and B Streptococcus species usually affect newborns. S. aureus, group A Streptococcus species, Haemophilus influenzae, and Enterobacter species affect children and adolescents. Adults may develop osteomyelitis because of S. aureus and occasionally Enterobacter or Streptococcus species.
Signs and symptoms of osteomyelitis
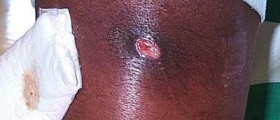
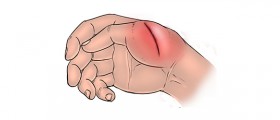
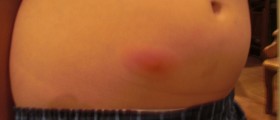
Signs and symptoms of osteomyelitis typically include fever, chills and pain in the infected region. Swelling, warmth and redness around the affected area are also common. Patient may be extremely irritable or lethargic, and complain about general discomfort, uneasiness or malaise. In some cases, osteomyelitis will be completely asymptomatic, or it will manifest in general symptoms that may resemble many other health conditions. For this reason, it is very important to seek medical attention whenever the bone pain worsens and presents itself along with fever. Osteomyelitis is usually diagnosed based on blood and imaging tests but bone biopsy is often necessary to determine what type of germ causes the infection.
Treatment for osteomyelitis
The backbone of the treatment is antibiotics. Surgery is also very important as it helps to remove infected or dead parts of the bone. Sometimes, doctors will only drain the infected area while in other cases it may be necessary to remove diseased bone and tissue and restore blood flow to the bone.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...