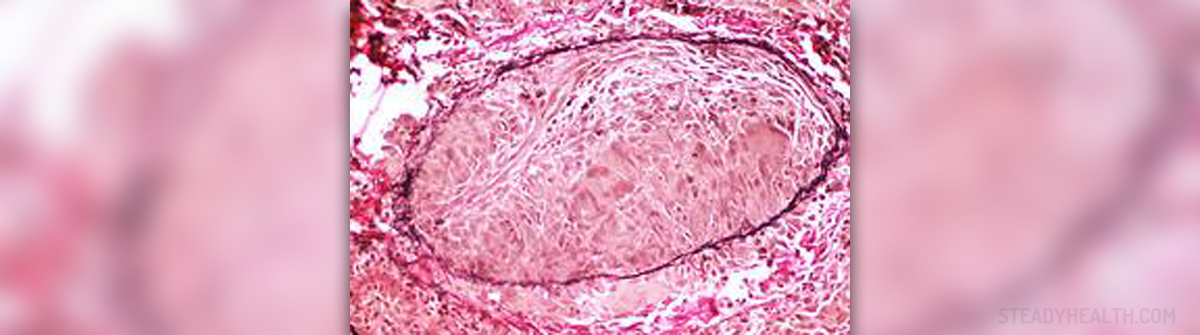
Chronic granulomatous disease is rare and quite severe genetic disease. It develops as a consequence of inadequate functioning of phagocytes, the type of white blood cells in charge with ingestion of harmful foreign particles like bacteria or dead/dying cells. Because these cells do not function properly the affected individual is highly susceptible to severe infections.
Chronic Granulomatous Disease: Causes and Risk Factors
Chronic granulomatous disease is a genetic disorder, meaning that it is transmitted from parents to their child. The defective genes are transmitted and because of them a person's immune system cannot kill pathogens like bacteria or fungi . This allows such microorganisms to multiple uncontrollably in the body and cause detrimental effects on many organs and organ systems. Patients are doomed to chronic and repeated infections.
This medical condition is diagnosed during early childhood. Only if the condition is not severe it may first occur in adolescence or adulthood.
Patients suffering from chronic granulomatous disease are prone to impetigo, skin abscesses, furuncles, carbuncles, perianal and perirectal abscesses. Recurrent pneumonia is another health issue such individuals have to face with. Chronically enlarged neck lymph nodes and subsequent abscess formation in them is another possible presentation of the disease.
This genetic condition is in a half of people transmitted in a recessive manner (transmission linked to sex chromosome). Because boys have only one X chromosome and this is the chromosome containing the defective gene it is clear that all boys with the defective gene are going to develop the disease. In girls since there are two X chromosomes, the healthy one prevents the occurrence of the condition. Still, the presence of the defective gene on the other chromosome allows further transmission of the disease.
Chronic Granulomatous Disease: Clinical Characteristics
There is a variety of infections such patients have to deal with. For instance, there are infections of the skeletal system (predominantly bones), various skin infections (abscesses, furuncles, impetigo, carbuncles etc.), chronic infections of the nasal cavity, perianal abscesses and persistent diarrhea. Such individuals often develop pneumonia which is generally hard to treat. If one develops abscess of the previously enlarged lymph nodes of the neck, he/she requires surgical drainage of accumulated pus.Chronic Granulomatous Disease: Diagnosis and Treatment
Apart from confirming the infection of different organs and organ systems, in order to definitely confirm the condition doctors need to perform flow cytometry tests and nitroblue tetrazolium test (NBT) which confirms the disease and may also detect mothers carriers of the disease.
There is no cure for this condition. Still, patients are treated aggressively with potent antibiotics or antifungal medications. The goal of the treatment is to eradicate the infection and prevent its recurrence. This is why medications may also be administered prophylactically. Severe infections are treated with interferon-gamma. Abscess requires surgical drainage. Finally, patients may significantly benefit from bone marrow transplant.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...