What is Staph Infection?
Staph infections are various infections affecting different organs and organ systems all caused by the Gram-positive coccal bacterium Staphylococcus aureus. The bacteria may be present on the skin of certain people and cause no harm. These individuals are known as carries and may easily transfer the harmful microorganism to healthy people triggering infections. This is why even though carriers are actually not ill, they need to receive a course of antibiotics which eradicates the bacteria.
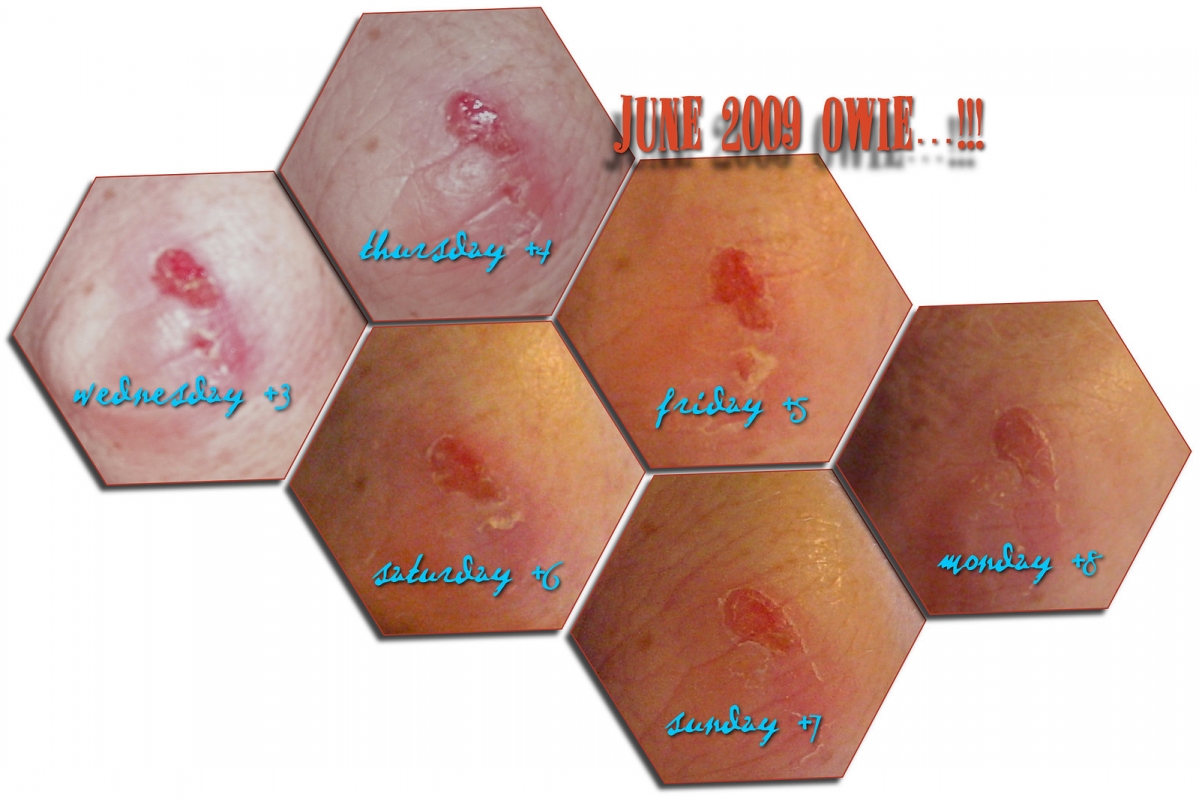
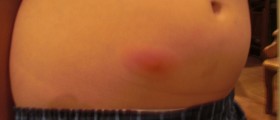
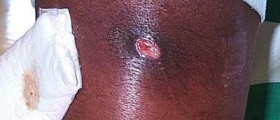
Skin infections caused by Staphylococcus develop after the bacteria penetrates the wounds or any cut that exists on the skin. The skin infections may range from pimples, boils (furuncles and carbuncles), impetigo to cellulitis, folliculitis, scalded skin syndrome and abscesses in which subcutaneous tissue gets affected as well. The bacterium may also enter the body, reach certain organs and organs systems causing their inflammation. For instance, there are Staphylococcal pneumonia, meningitis, osteomyelitis, endocarditis, toxic shock syndrome and bacteriemia/sepsis.
How do People Get Staph Infections?
It is possible to contract the harmful bacteria from contaminated surfaces. Interhuman transfer is also an option. People who are carriers spread Staphylococcus aureus via dirty hands/fingernails. Because of that the best prevention possible is through frequent hand washing. Kids are especially encouraged to learn how to maintain proper hygiene of their hands, wash them with warm water and soap several times per day, especially prior to consuming food and after using the toilet.
Also, contamination may be accidental when bacteria enter the open wounds, or scrapes. The damaged skin is supposed to be kept clean and if necessary, covered with sterile bandage.
Serious Staph Infections
Folliculitis, furuncles and carbuncles are relatively moderate infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus. In folliculitis the infection affects hair follicles. The surrounding skin is inflamed and red. Folliculitis typically occurs in the skin areas that are exposed to friction and irritation such as beard in men and legs in women. Folliculitis may sometimes progress into boils. Boils are solitary lumps (furuncles) or several of them form clusters known as carbuncles, abscesses with more than one opening from which pus drains spontaneously.
Impetigo affects different portions of the skin predominantly the area round the mouth and nose. This skin infection is frequent among children and generally occurs during the summer months. The affected skin is covered with fluid-filled blisters. They may easily rupture, ooze and eventually get covered with a honey-colored crusts. Itching is another characteristic of impetigo. By scratching the affected skin, infection can be spread to nearby, previously healthy skin.
When it comes to serious infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus there are several worth of mentioning.
Scalded skin syndrome is, for example, a complication of a localized staph infection. It affects newborns and is frequent among children under the age of 5. The toxin produced by the bacteria is blamed for general ill-feeling, headaches, confusion, high fever accompanied by chills, low blood pressure and muscle aches. Some children feel nauseated, vomit and suffer from diarrhea. It is also possible to develop seizures. The condition requires hospitalization and aggressive antibiotic treatment.
Cellulitis occurs once the infection from the skin spreads to deeper layers, predominantly subcutaneous tissue. It is also a complication of a localized staph infection and can additionally cause new health issues among which sepsis is the most severe one.
Staph food poisoning occurs once the food gets contaminated with the bacteria. The bacteria multiplies and synthesizes a toxin. The food does not smell bad and shows no signs of being spoiled. The severity of symptoms and signs are closely connected to the amount of ingested toxin. Initially, there are nausea, vomiting, and stomach cramping. Diarrhea may occur too. More complex cases of food poisoning are accompanied by dehydration, headaches and muscle aches. There is also a drop in blood pressure or pulse rate. Fortunately, most patients fully recover after 2-3 days.
Finally, there is MRSA infection, definitely one of the most severe infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria resistant to many available antibiotics. This bacterial strain can be isolated in people who are hospitalized or those living in nursing homes. Also, MRSA may affect previously healthy individuals.
Staph Infections Treatment Options
In the majority of cases superficial skin staph infections can be easily dealt with an antibacterial cleanser, warm soaks and antibiotic ointments. The affected area should be covered with a sterile and clean dressing. The tower that is used for cleaning the area must never be shared with other people and is supposed to be washed immediately.
More complex staph infections require oral antibiotics and sometime patients even need to be hospitalized. MRSA is the most challenging infection of all staph infections and may be only eradicated with antibiotics to which the bacteria is still sensitive.
And finally, staph infections can be successfully prevented if one maintains impeccable hand hygiene, keeps the damaged skin (wounds, cuts, scrapes, eczema etc.) clean and covered. Also, if the infection has already developed, the person must never share towels, sheets or clothing until the bacteria is completely eradicated.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...