Hemophilia is a blood disorder that manifests in problem with blood clotting. The clotting process is a course in which the blood changes from liquid to solid state. This is one of the most important bodily processes that help to stop bleeding or the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel. Hemophilia is a hereditary genetic disorder that exists in two major forms. Hemophilia A (also known as clotting factor VIII deficiency) is the most common form that occurs in 1 in 5,000–10,000 male births. Hemophilia B (also known as clotting factor IX deficiency) occurs at 1 in about 20,000–34,000 male births. Only in some rare cases, females are born with hemophilia. Causes of hemophilia
Deficiency in platelets or one of the procoagulant plasma proteins that are responsible for blood clotting causes hemophilia. The exact type of hemophilia depends on which clotting factor is deficient. In the most common, hemophilia A, patient is lacking clotting factor VII. In the case of hemophilia B, patients are deficient in clotting factor IX, while people with hemophilia C suffer because of a lack in clotting factor XI. Since it is a hereditary disorder, it is normal that certain subtypes are more frequent in certain parts of the world. Therefore, hemophilia C is the rarest type in the United States. However, this is the mildest of all forms and easiest to manage.
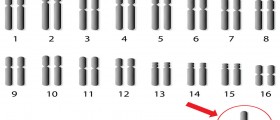
The gene responsible for hemophilia is located on the X chromosome. Females inherit two of these chromosomes: one from mother and one from father. Males inherit one X chromosome from mother and Y chromosome from father. Therefore, hemophilia occurs in boys, since they have just one X chromosome. Females, however, may have a defective gene and another X chromosome to substitute. Therefore, females will pass the gene to their offspring, but they will not exhibit the signs of disease themselves. Only hemophilia C occurs in both boys and girls.
Signs and symptoms of hemophilia
In general, signs and symptoms of hemophilia depend on the actual deficiency in clotting factors. If the deficiency is very mild, patients may bleed only after some kind of trauma to the body tissues. If the deficiency is severe, there may be spontaneous bleeding.
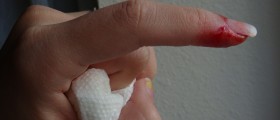
Spontaneous bleeding manifests as unexplained bleeding or bruising accompanied with many large and very deep bruises. Sometimes, the joints may hurt and may become swollen because of internal bleeding. Patient may also notice blood in the urine or stool. Nosebleeds are also frequent and bleeding after a simple injury is often excessive and prolonged.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...