Introduction
Duodenum is a part of the gastrointestinal tract that plays a vital role in the digestion of food. After the food is consumed, it passes through the esophagus into the stomach, where it is partially digested with the help of the stomach acid. Then the food passes into the duodenum, which is the first part of the small intestine.
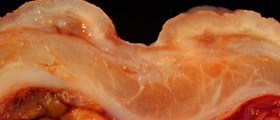
Duodenal ulcer, which is a peptic ulcer located in the duodenum, is one of the most common health problems related to the duodenum. In fact, this type of peptic ulcer is more common than the stomach ulcer. Peptic ulcers result from inflammation caused by the stomach acid. The inflammation causes damage on the wall of the duodenum, exposing the underlying tissue. An ulcer usually looks like a small red crater on the wall of the duodenum and it can be extremely painful.

Causes of duodenal ulcers
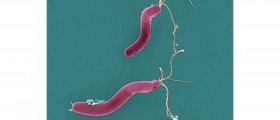
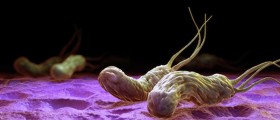
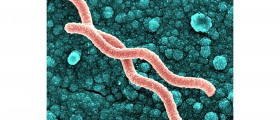
Stomach acid is corrosive and it can be harmful for the cells of the duodenal walls. In a healthy duodenum, there is a balance between the amount of acid and the natural protective barrier of the walls. In some situations, the balance is disrupted and the acid starts damaging the cells and tissues of the duodenal walls. Of all the causes that may lead to this, infection with Helicobacter pylori is the most common. Many people have this bacterium in their gastrointestinal tract but not all of them develop an infection. If the infection is not properly treated, it becomes chronic and permanent and significantly increases the risk of duodenal ulcers.
Another major contributor to duodenal ulcer is overuse of certain anti-inflammatory drugs, especially Aspirin. These drugs alter the mucous barrier of the duodenum and increase the chance of damage that leads to formation of ulcers.
Symptoms of chronic duodenal ulcer
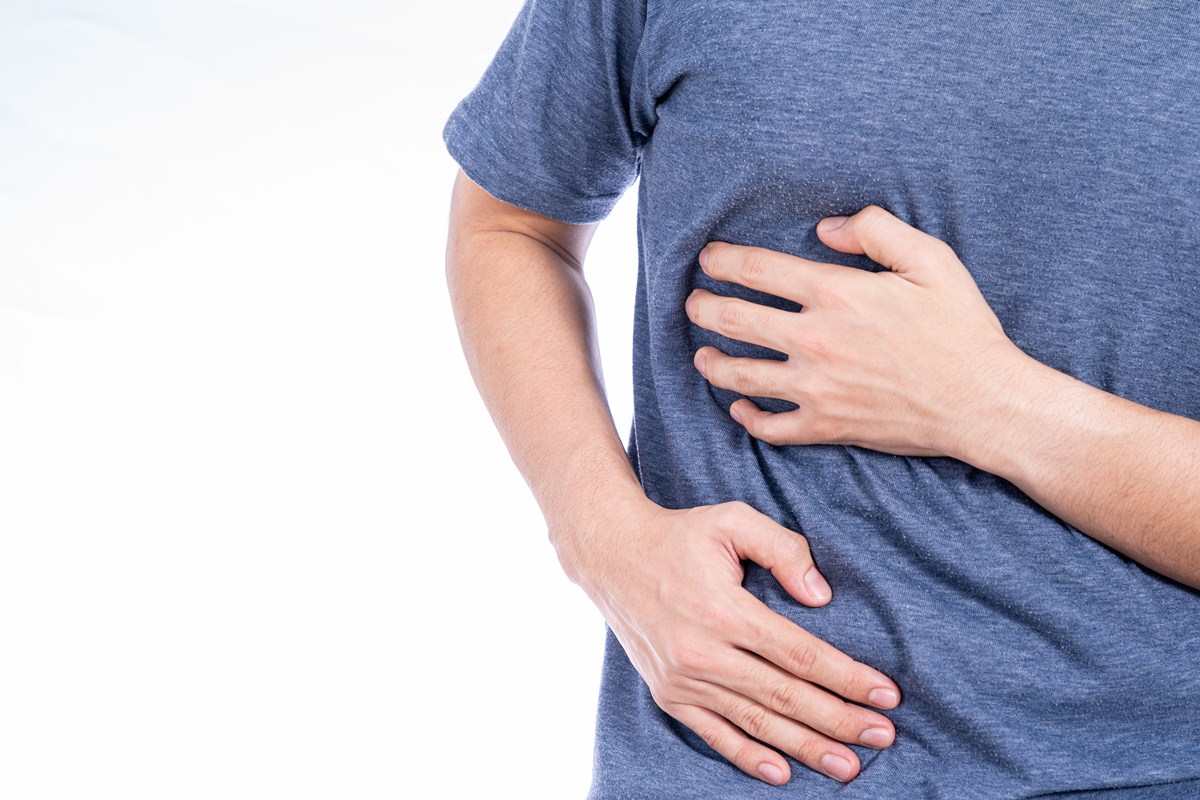
The symptoms of duodenal ulcer, both chronic and acute, include pain just below the chest bone, that usually comes and goes. It may become worse before meals, when the stomach is empty and can be alleviated with food or with the use of antacids, which are used for heartburn. Other symptoms may include bloating, belching and nausea.
Chronic duodenal ulcer may lead to serious complications. The most common complications are bleeding, which can be minor and harmless, or major and potentially life-threatening, and perforation, which causes very severe pain and is considered a medical emergency.
Chronic duodenal ulcer must be taken very seriously. The treatment may consist of medication or surgery, as well as certain lifestyle and dietary changes. The most important thing is to determine what is causing chronic ulcers and to resolve those issues.
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/stomach-ulcer/
- Photo courtesy of SteadyHealth








Your thoughts on this
Loading...