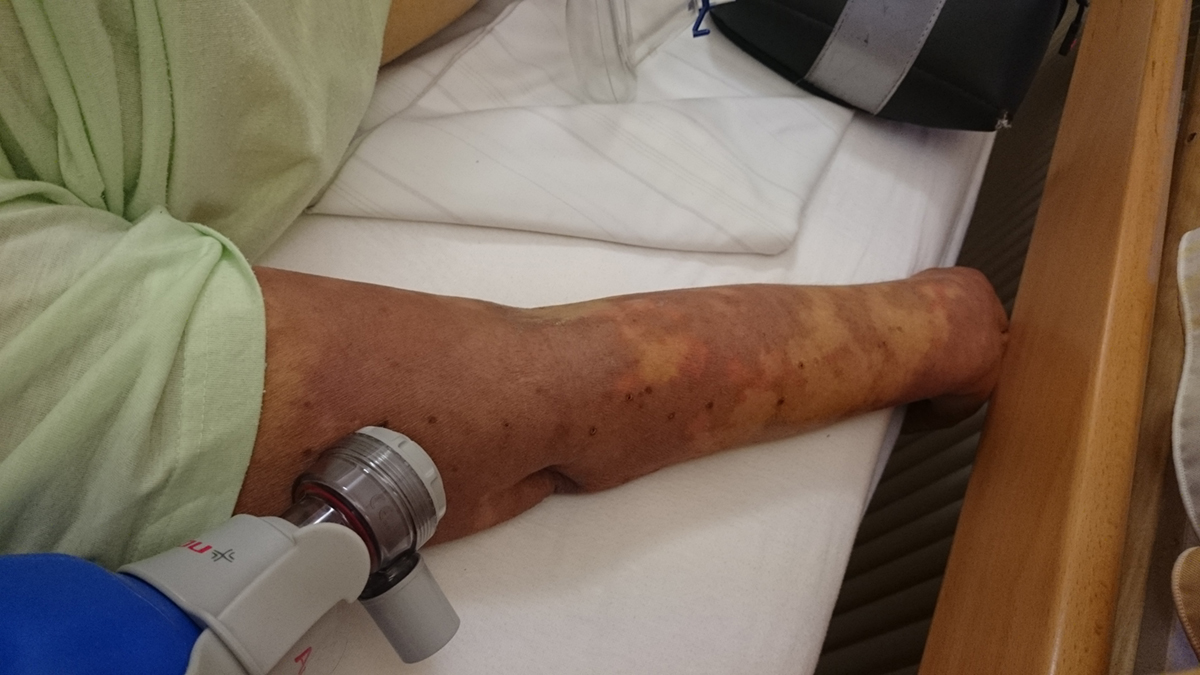
Sepsis is an extremely serious health condition distinguished by a whole-body inflammatory state and the presence of an infection. Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition because body’s own immune reaction to the present infection may do the serious damage to body tissues. Other term for sepsis, that greatly illustrates the seriousness of this condition, is “the blood poisoning”.
Causes of sepsis
Sepsis infection may occur because of the presence of microbes in the blood, urine, lungs or other tissues. Body normally reacts to the infection by inflammation. However, in sepsis, the inflammatory process becomes exaggerated, and spreads beyond the infection site. Inflammation may affect the whole body. Microscopic blood clots form in the blood vessels while the inflammatory response obstructs body’s natural ability to produce anti-coagulants. The resulting effect is failure of the organs that occurs from the inability of oxygen to reach the living tissues. Even as the heart pumps blood harder, the blood clots are preventing the oxygen to reach the organs and the failure is inevitable.
Symptoms of sepsis
Symptoms of sepsis may vary depending to the seriousness of the infection. Sepsis symptoms are usually developing through three stages: sepsis, severe sepsis and septic shock.
Sepsis is characterized by the presence of at least two of the following symptoms: abnormal bodily temperature that may be higher than 101.3˚ F or 38.5˚ C, or less than 95˚ F or 35˚ C; increased heart rate, higher than 90 beats per minute; hyperventilation with respiratory rate higher than 20 breaths per minute; probability or confirmed infection.
Second stage of sepsis involves additional set of symptoms that may point out to organ dysfunction. These symptoms include: patches of spotty skin, reduction in urine output, changes in cognitive functions, low levels of thrombocytes, heavy breathing or difficulties to breathe, and abnormal heart functions.
Septic shock, as the most severe stage of sepsis, can cause multiple organ dysfunction syndrome and death. Symptoms of septic shock include all of the symptoms of severe sepsis plus extremely low blood pressure.
Prognosis and treatment of sepsis
If the sepsis is recognized and treated in the early stage, patients may significantly improve their chances of survival. Early treatment usually involves large amounts of intravenous fluids and antibiotics. Antibiotics may significantly slow the rate at which infection develops and they usually give doctors additional time to carry out the further examinations. Sepsis is usually treated in hospitals, and in severe cases patients are shifted to the intensive care units.
Death rate associated with sepsis is very high. It is estimated that sepsis has fatal consequences in approximately 60% of all cases. However, accurate prognosis depends on the patient’s age and general health condition. Death rate in otherwise healthy people is reasonably low – about 5%.









-Arthritis_f_280x120.jpg)
Your thoughts on this
Loading...