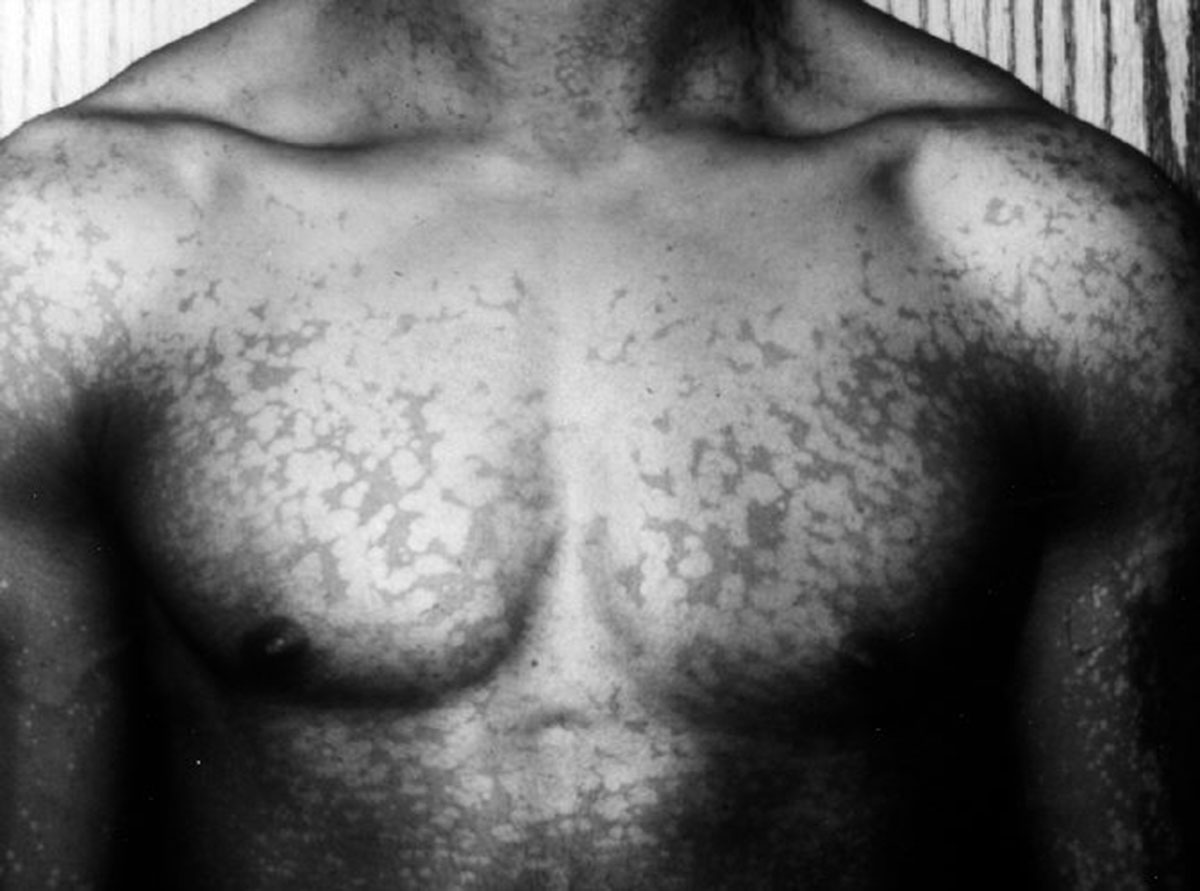
Pityriasis rosea is the non contagious skin rash. It generally affects teenagers and young adults. The skin changes last approximately six weeks and they withdraw completely. In rather rare cases this skin rash may linger for 12 weeks. The disease cannot affect the same person twice.
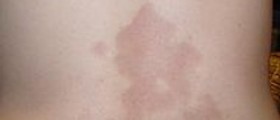
The onset of the disease is typical. A person may notice a single patch on the skin. This is a red or pink patch with the size ranging from 2 to 10 centimeters. This specific skin change is known as herald patch. It predominantly affects the back, the chest or the neck. The patch is also referred to as mother patch. Two weeks after the initial patch has occurred a person starts to develop numerous smaller patches all over the trunk and the extremities. This is actually the second stage of the disease. These secondary patches distribute symmetrically and their size is between 0.5 centimeters and 1.5 centimeters. These skin changes follow the specific pattern called 'Christmas tree' pattern and affect cleavage lines. The skin changes only distribute on the trunk and the extremities leaving the face, neck, hands and feet clean.
Symptoms of Pityriasis Rosea
Apart from the previously mentioned rash a patient does not have to complain about additional symptoms or signs of the disease. The skin changes may be itchy especially after baths or after exercises. This medical condition may be accompanied with soar throat, tiredness, nausea and aches. Some people even complain about the loss of appetite.
Causes of Pityriasis Rosea
The cause of pityriasis has not been established yet. Still, some researches have connected this condition with the infection caused by human herpes virus type 6. There is no obvious connection between pityriasis rosea and herpes viruses that cause oral and genital herpes infections.
Some believe that transmission of pityriasis rosea is possible via respiratory contact. Still this disease generally has not been transmitted from the affected person to people from his/ her surrounding.
Pityriasis is definitely not related to allergies of any kind or other illnesses including infections.
Diagnosis of Pityriasis Rosea
The onset of the disease together with pattern of the skin patches helps the doctor to set the diagnosis. The initial patch is very specific for the disease.
Additionally, doctor can set the diagnosis of pityriasis rosea if he/ she rules out the possibility of other skin conditions such as fungal infections. This can be done by simple skin tests. Even other skin conditions such as syphilis can be ruled out by specific blood tests. In rather rare cases the doctor will perform a biopsy of the affected skin.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...