About Guillian Barre Syndrome
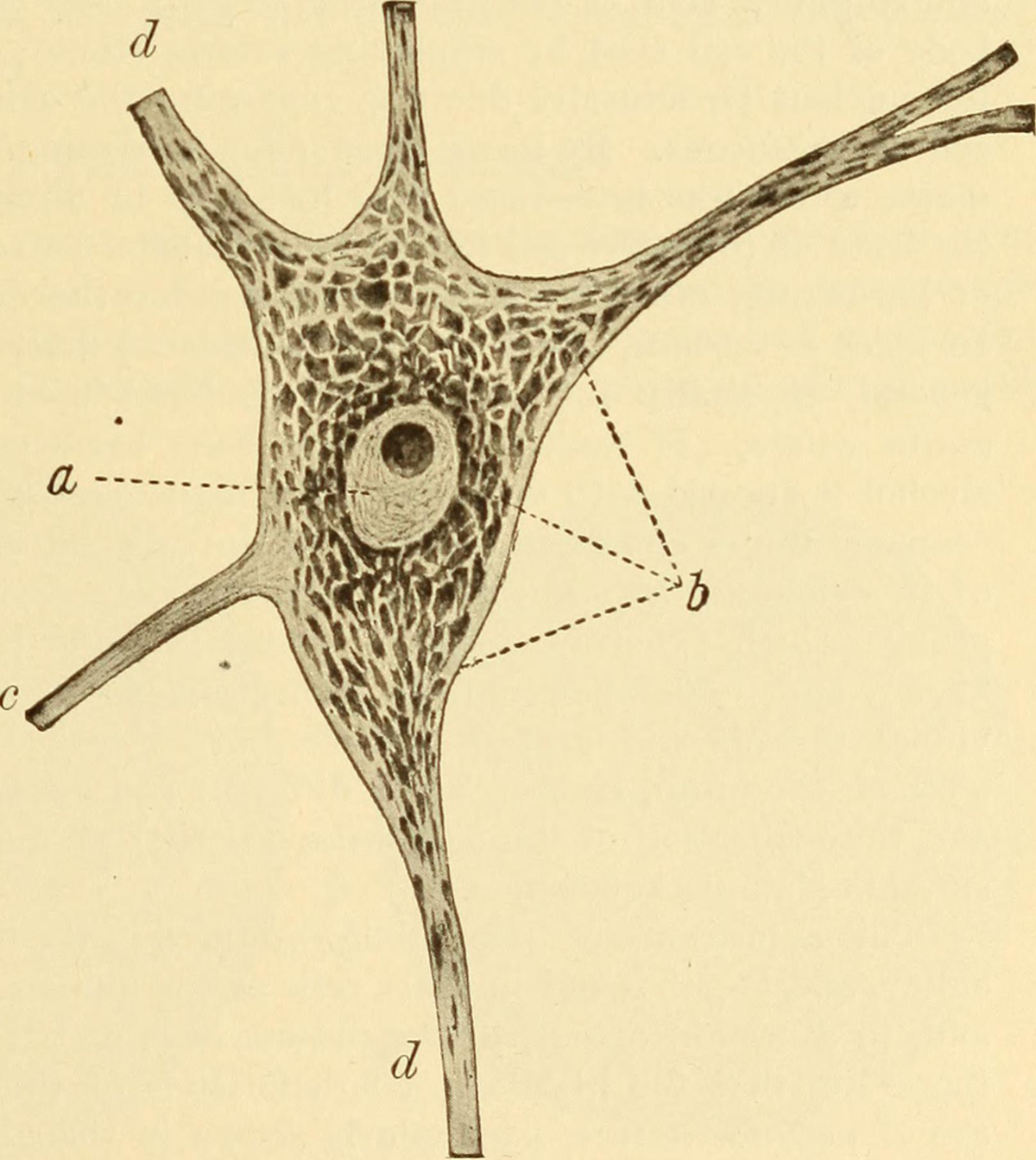
Guillian Barre is an acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, an uncommon disorder that develops due to damage of the peripheral nervous system. The patient's body attacks the nerves and this leads to their damage which eventually results in weakness, numbness in the extremities and in terminal stage paralysis of the entire body.
The actual cause of Guillian Barre has not been identified yet but it has been noticed in many patients that the disorder develops after an infection of either the lungs or the digestive tract. In other patients the condition develops without any noticeable trigger.
In the initial stage patients suffering from Guillian Barre develop weakness, tingling sensation or loss of sensation that starts in the legs or feet. These sensations spread further to the upper parts of the body. The symptoms may be at first localized in fingers and toes and simply neglected. There are also the cases when the symptoms first affect the upper extremities or the face. Progression of the disease eventually leads to difficulties with eye movement, facial movement, speaking, chewing and swallowing, unsteady walking, inability to walk and paralysis. Patients additionally complain about severe pain in the lower back, they develop problems with bladder control and intestinal functions and may suffer from breathing difficulties.
Therapy for Guillian Barre Syndrome
Some patients suffering from Guillian Barre syndrome may need months and years to recover. However, in majority of cases the condition follows the specific pattern. Namely, after the onset of the initial symptoms and signs they progressively worsen and this lasts for approximately two weeks. After that the symptoms and signs remain unchanged for about 2-4 weeks and finally patients enter the recovery phase that may take 6-12 months.
Unfortunately, there is no cure for Guillian Barre syndrome. Still, the severity of symptoms can be reduced with two types of treatments. The recovery can also be accelerated with these treatments. The first one is plasmapheresis. This is a form of plasma exchange in which antibodies responsible for the damage are removed from the blood. Other treatment includes intravenous administration of immunoglobulin. High doses of immunoglobulin may be effective against damaging bodies the body produces.
It is essential to carefully monitor each patient in the initial stage of the disease. Breathing problems as well as other life-threatening complications usually develop within 24 hours after the onset of the disease. Patients with quick progression of muscle weakness require admission to a hospital or intensive care unit. After recovery has started patients engage in physical therapy which helps them restore muscle strength and movement.







-And-Multiple-Sclerosis-Differences-And-Similarities_f_280x120.jpg)







Your thoughts on this
Loading...