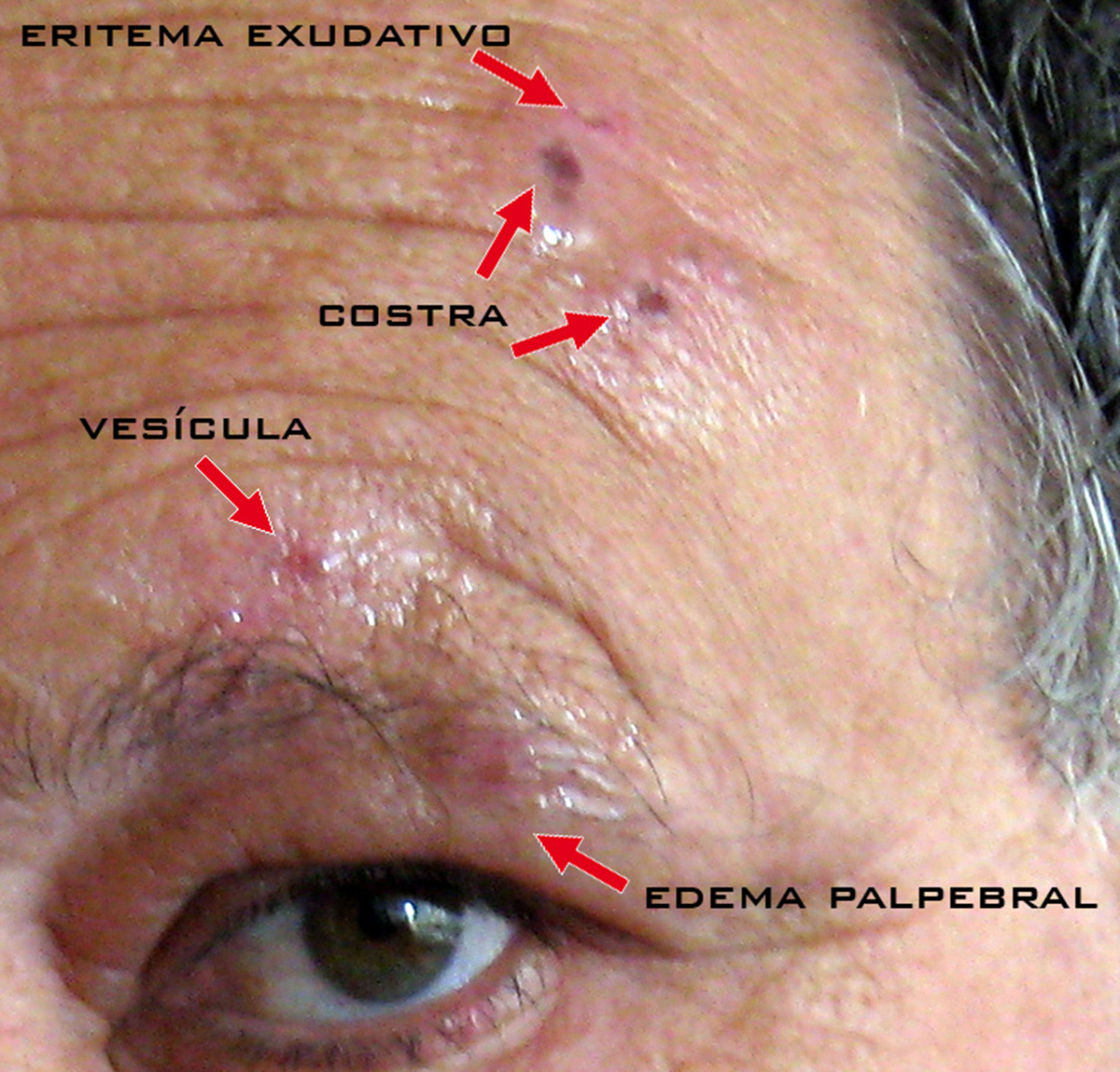
Herpes zoster oticus, also known as Remsay Hunt syndrome, represents a complication of shingles. Shingles are caused by Varicella zoster virus, the same one that causes chickenpox. Shingles occur later in life; years after the person had chickenpox. The virus is somehow reactivated and the disease affects different parts of the skin causing formation of skin rash and painful blisters. In case of herpes zoster oticus the virus spreads to the facial nerve and sensory nerves innervating the ear.
Causes of Herpes Zoster Oticus
Reactivation of dormant Varicella zoster virus leads to the onset of herpes zoster oticus. This medical condition predominantly affects immunocompromized patients and people with weak immune system such as patients suffering from HIV infection, carcinoma, and those who have recently undergone radiation or chemotherapy. Physical and emotional stress is considered potential triggers as well.
Symptoms and Signs of Herpes Zoster Oticus
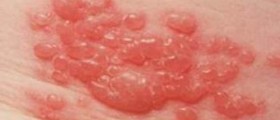
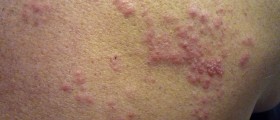
The leading symptom of herpes zoster oticus is pain deep inside the ear. The pain is in the beginning paroxysmal and after a few days it begins to radiate toward the outside of the ear, the auricle. Furthermore, painful red rash covers the inside of the ear and the eardrum. The rash may also affect the pinna, the roof of the mouth and the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. Additional symptoms include hearing loss and problems with balance, tinnitus and dizziness. Due to affection of the tongue a patient may complain about loss of taste or changes in taste perception. Since the facial nerve is affected there are signs of facial weakness or facial palsy (droopy eyelid and inability of a person to frown, show his/ her teeth and close the affected eye).
Diagnosis and Treatment for Herpes Zoster Oticus
Diagnosis of herpes zoster oticus can be easily set thanks to typical symptoms and signs of the disease. The doctor asks the patients about all the complaints and after performing an ear examination he/she may notice an obvious sign of the disease, typical herpes zoster rash. Neurological examination is necessary for evaluation of potential complications such as hearing loss, facial paralysis and changes in taste.
Patients are treated with antiviral medications, corticosteroids and pain relieving medications. Antiviral medications are highly effective in reduction of the symptoms and signs of the disease and they may accelerate the recovery. Unfortunately, some symptoms such as hearing loss or facial paralysis may be permanent.
It is essential to start with treatment immediately after setting of the diagnosis. These way long-term complications can be successfully prevented.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...