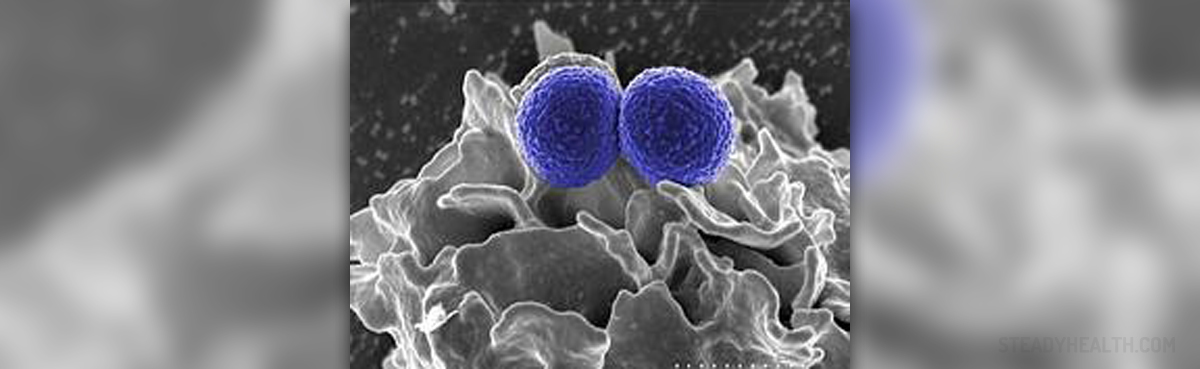
MRSA is short for Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, the bacterium which causes severe infection and is quite resistant to almost every antibiotic. Staphylococcus aureus is sometimes found on the skin and inside the nasal cavity of some individuals. The bacterium did not use to be such a problem until it developed resistance to many different and previously potent antibiotics. This has led to a severe problem, development of an infection which is today hard to eradicate. Infections caused by MRSA affect people of all ages. MRSA infection has shown drastic increase in children. It is estimated that a number of MRSA infections affecting the neck and head in children has doubled within the period of 5 years. Because of that it is essential to get familiar with prevention of MRSA infection.
MRSA Infections in Children - Causes
The infection is not only reported in children with weak immune systems (although such children are more susceptible), it affects healthy children as well. Increased number of community-associated MRSA (infections that occur outside of hospitals and nursing homes) gives rise to new cases of the infection among children. In majority of cases the bacterium is responsible for skin infection.
Children may contract the bacterium in day care centers, on playgrounds, in locker rooms, classrooms and other school settings. It is also possible to get infected in gymnasiums. Children with skin-to-skin contact as well as those prone to sharing contaminated equipment equipment are at higher risk of contracting the bacterium.
MRSA Infection in Children - Clinical Characteristics
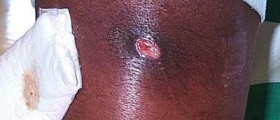
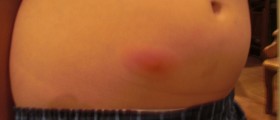
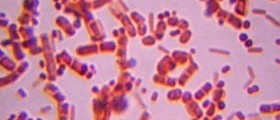
The affected skin is red, swollen, warm to touch and rather painful. There is evident pus collection or the pus drains from the wound. Fever and malaise occur as well. The infection most commonly affects the area that has previously been injured (wounds, cuts or scrapes). The doctor will need to examine other family members too, in order to exclude transmission of the infection. Definitive confirmation is achieved after laboratory testing of taken samples (skin culture, culture of the draining fluid, blood culture, sputum culture or urine culture).
MRSA infection in Children - Treatment
Treatment includes draining skin abscesses, if there are any, and prescribing potent antibiotics, the ones the bacterium is still sensitive to.
In order to prevent further transmission of bacteria, bandage is supposed to be changed frequently and while doing this and during cleaning of the wound it is best to wear gloves. Used bandages must be carefully disposed. After changing bandages, hands should be thoroughly washed. Alcohol-based sanitizer is also recommended.
Parents can prevent infection in case they teach their children to frequently wash their hands with soap and water, especially after playing with pets and other children. Furthermore, if washing is not possible, one should use alcohol-based sanitizers or wipes. Children are not supposed to share towels or other personal items. In case of cuts and wounds the affected skin should be properly cleaned and covered with dry bandages until it adequately heals.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...