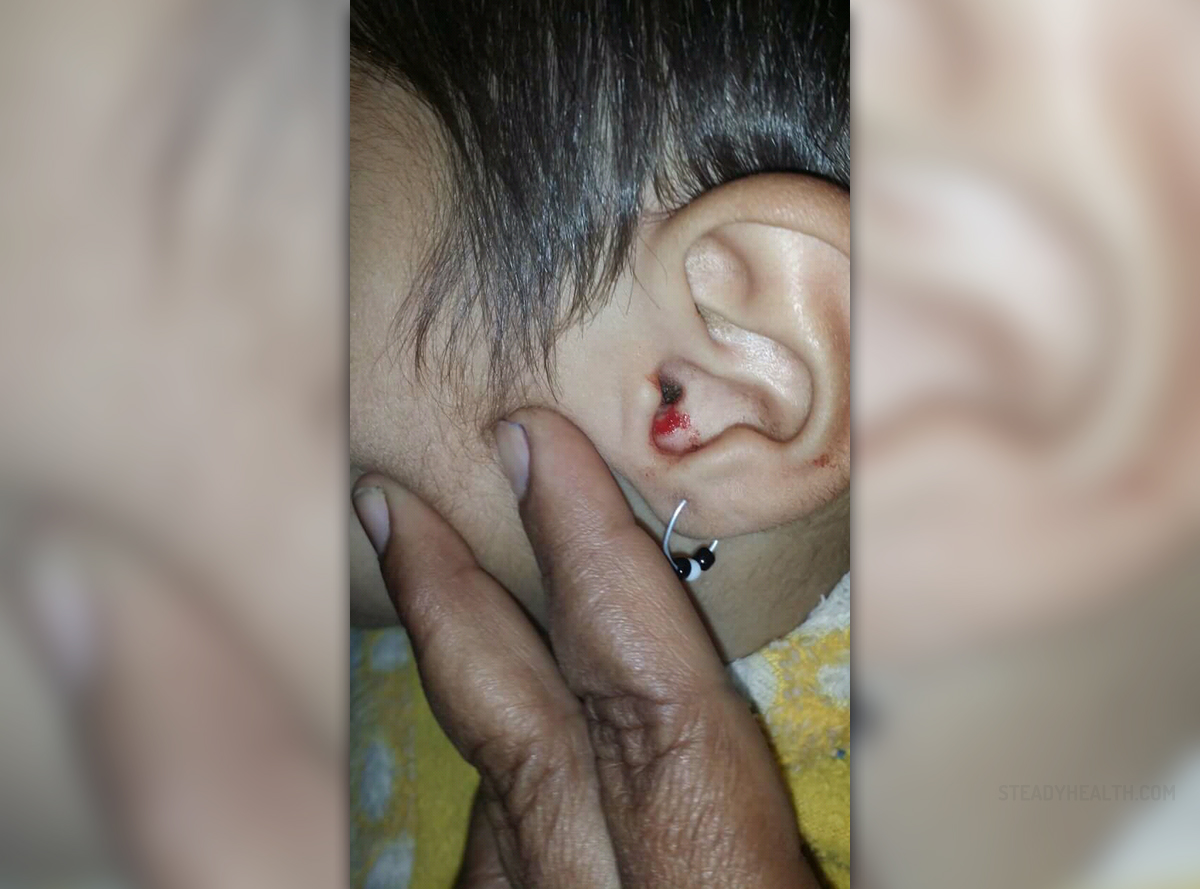
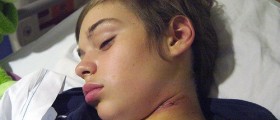
Extremely fragile skin is the main characteristic of the skin condition known as epidermolysis bullosa or just EB. This condition is very rare and just 1 out of every 17.000 of newborns, both boys and girls, is born with this problem or develops it short after the birth. As mentioned, EB is inherited and the child commonly inherits faulty gene from one or both of his parents. Depending on the type of EB, sometimes the person must have both copies of faulty gene or just one in order to express the symptoms of this disease.
What Causes Epidermolysis Bullosa?
The human skin has three different layers the epidermis, dermis and subcutis and the first two, the outer and middle layer (epidermis and dermis), have some proteins responsible for maintaining these structures together. If some of these proteins do not work properly, due to genetic mistake (faulty gene found in EB), any friction of the skin or trauma may result in separation of epidermis and dermis and formation of blisters.
Series of faulty genes are found to cause epidermolysis bullosa. Symptoms of this skin condition, therefore, depend on the types and effects of mutations of genes to layers of the skin. These mutations can be inherited as either autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Autosomal dominant characteristic (or in this case symptoms of epidermolysis bullosa) are expressed when a person inherits just one faulty copy of genes. His or her parent (with mutated gene) also has similar symptoms. Autosomal recessive characteristics are expressed only if both copies of the gene responsible for EB contain mutations. Neither parent has any problems or symptoms of epidermolysis bullosa, but the child dpes.
Types of Epidermolysis Bullosa
EB has three main types, including epidermolysis bullosa simplex (EBS), junctional epidermolysis bullosa (JEB) and dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB). Besides these, there are also variants of three main types and doctors have identified 27 subtypes so far.
Epidermolysis bullosa simplex patients have blisters in the epidermis of the skin and this type accounts for about 70% of all diagnosed cases of EB. Dystrophic EB affects the epidermis and upper parts of the dermis and it is identified as the cause in about 20% of EB patients. Junctional EB is known to affect the skin between epidermis and dermis and this is the most serious type of epidermolysis bullosa doctors know, reported in 5% of cases.
Children of people suffering from EBS have 50% chances to inherit this condition, while the problem is less likely to be passed onto kids if the person has DEB or JEB.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...