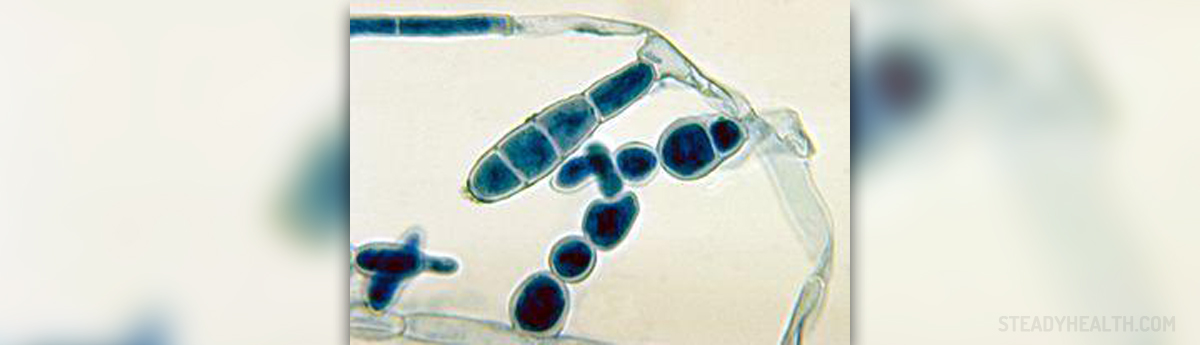
Epidermolysis bullosa can be subdivided into four categories. These categories are known respectively as dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, epidermolysis bullosa simplex, hemidesmosomal epidermolysis bullosa, and junctional epidermolysis bullosa. There is, however, another rare form of epidermolysis bullosa, which is known as epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. This is an autoimmune disorder, and it can be difficult to distinguish this condition from another disorder, known as mucous membrane pemphigoid.
About epidermolysis bullosa
The condition can be minor in form. This form can lead to minor blistering of the skin, but also to a lethal form of the condition that can involve other organs. For the most part, this condition begins at birth. However, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita normally occurs in those over the age of fifty. It can be difficult to identify the exact type of epidermolysis bullosa that has become manifest in an individual. It is important to note that even though there are four main types of the condition, there are many subtypes that exist within these major types.
In general, epidermolysis bullosa is an inherited condition. Thus, a family history of epidermolysis bullosa should be considered a significant risk factor when it comes to the development of the condition in a given individual. Inheritance can be dominant or recessive. Dominant means that a child can inherit the disease even if only one parent suffers from the condition. On the other hand, recessive means that both parents must carry the relevant gene in order for the condition to develop in the child.
The recessive form tends to be worse. The main indicators of this condition is the formation of large, fluid-filled blisters that develop in response to trauma. In some cases, infants might have blisters that develop from birth. Chafing, rubbing, or even increased room temperature can lead to the formation of blisters.
Treatment
For the most part, treatment is centered around the prevention of blister formation and the resultant complications. The level of treatment will depend on the severity of the disease. In order to prevent infection, it is vital that skin care is properly undertaken, particularly in the event that blistered areas become crusted or denuded. Regular whirlpool therapy and the application of antibiotic ointments can be beneficial in this regard. If a patient is suffering from difficulties related to swallowing, then the use of oral steroids might be recommended. It is also important to maintain dental hygiene. Thus it is vital to regularly consult dentists who have experience in dealing with those who suffer from epidermolysis bullosa.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...