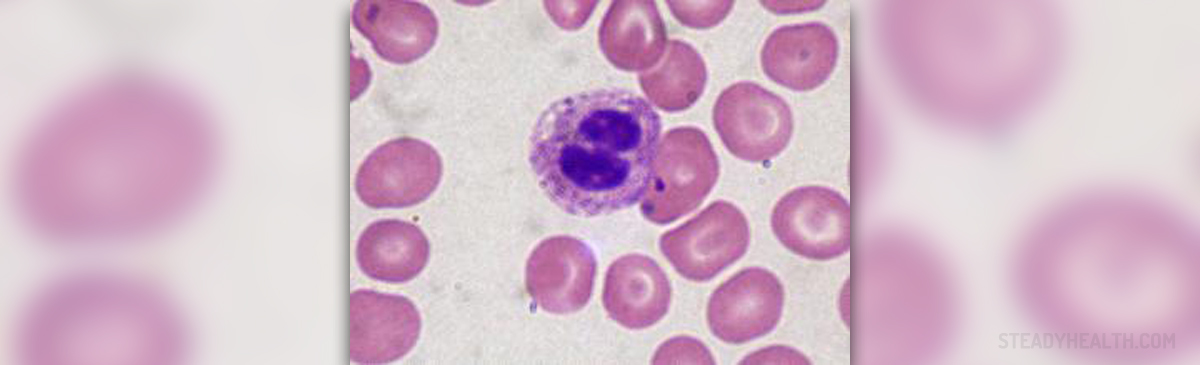
The myelodysplastic syndromes are various hematological health conditions distinguished by the ineffective production of myeloid blood cells. All of these conditions bare a strong risk of progressing to acute myelogenous leukemia. In a nutshell, these disorders are affecting the bone marrow stem cells, leading to ineffective blood production and defects in blood cells. Bone marrow is a place in the human body where the blood cells are being made. A disorder like this results in poorly formed or dysfunctional blood cells. These defective blood cells die in the bone marrow or instantly as they enter a blood stream. The problems start when the number of defective cells begins to suppress the healthy blood cells. For this reason, the main complications of the disease are anemia, infections, and excessive bleeding.
Causes of myelodysplastic syndromes
For many cases of myelodysplastic syndromes, doctors can’t find the obvious cause. These diseases are listed as “de novo myelodysplastic syndromes”. For approximately 60 to 70 percent of patients diagnosed with this disease, the cause isn’t obvious. The other possible cause are chemicals and radiation, as myelodysplastic syndromes often develop as a side-effect of cancer treatments, chemotherapy and radiation therapy, or chemical exposure.
Symptoms of myelodysplastic syndromes
This disease usually develops in the elderly population. On the average, people first diagnosed with myelodysplastic syndromes have somewhere between 60 and 75 years. The disease is very rare in population younger than 50. Signs and symptoms of the disease are nonspecific, and they could also point out to some other health disorder. Anemia is one of the major symptoms, accompanied with chronic fatigue, shortness of breath and chilled sensation. Low neutrophil count is also characteristic for the disease, and it makes a patient more prone to various infections. Low platelet levels are also present, and the patient may be susceptible to bleeding and unusual bruising. Very small red spots just beneath the skin may also be visible, as they result from bleeding.
Treatment
Unfortunately, there is no known cure for myelodysplastic syndromes. The treatment is concentrated on reducing the risk and preventing the complications of this disease. In some cases, patients may undergo a bone marrow transplantation surgery, which may significantly prolong their lives. Supportive care usually consists of blood transfusions aimed to replace blood cells. Medications used for treatment may increase the number of blood cell production, stimulate blood cells to mature, suppress the immune system or help with a genetic abnormality. In very rare cases patient will get a bone marrow stem cell transplant. Unfortunately, this procedure is very risky especially for older adults, and just a small number of patients are candidates for transplantation.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...