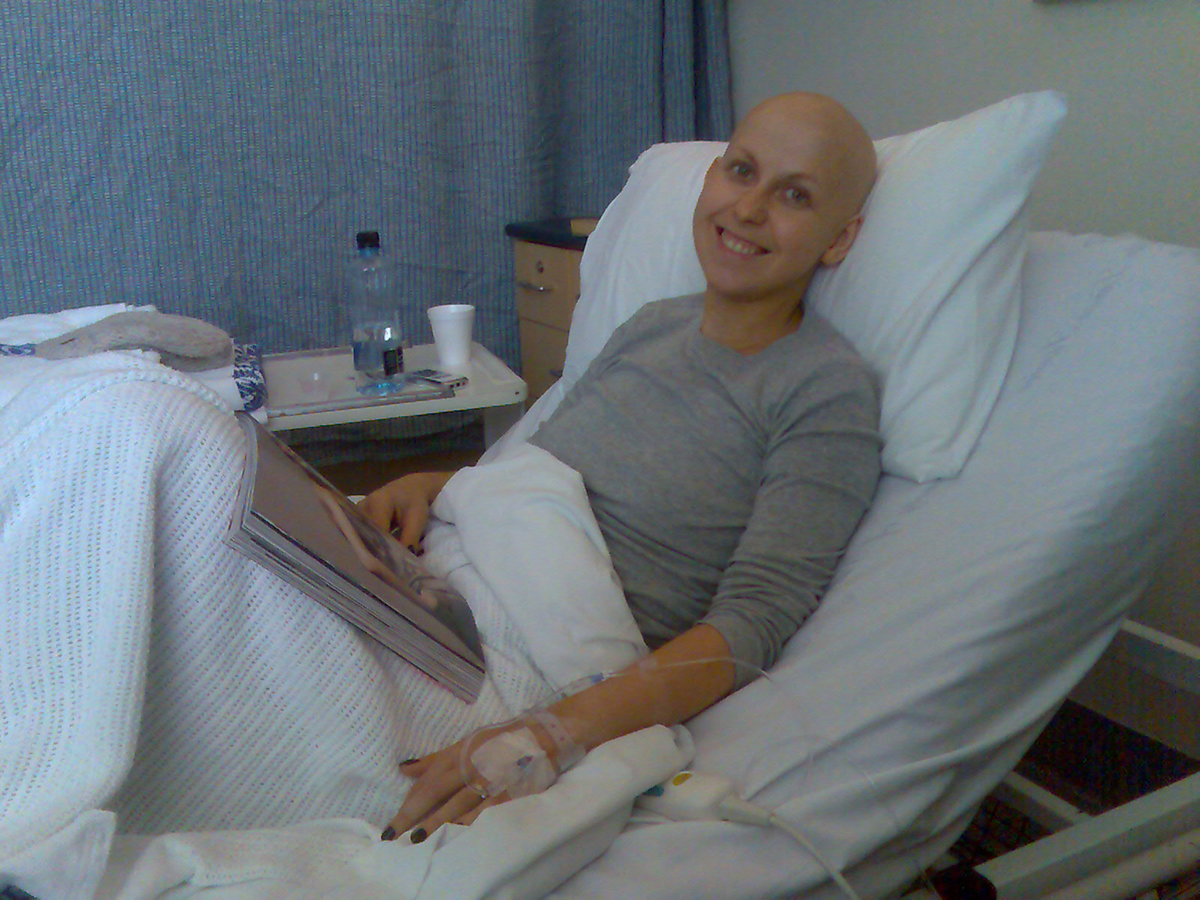
Small number of neutrophils in the blood is called neutropenia. Neutropenia is a medical condition that may cause highly risky infections that may end up with death. This condition can be caused by cancer, radiation therapy or chemotherapy. The main indication to neutropenia are often and strange infections. To diagnose neutropenia doctor takes a blood sample and bone marrow sample. Any further treatment of condition is determined by disease’s severity.
The diseased neutrophils make body more susceptive to acute bacterial or fungal infections. Neutrophils are having up to 75% of white blood cells. And risk for a bad infection gets to be higher if neutrophils count decrease under the 1,000 cells per microlitre of blood. And if this is under 500 cells per microliter, infection risk is very high. A lack of main defence in the body that is provided by neutrophils creates difficulty to control heavy infections that may cause death of patient.
Causes
Neutropenia annuls neutrophils faster then bone marrow production of new ones. Bacterial infections or a bad allergy may consume neutrophils quicker, so bone narrow haven’t got enough time to produce new. Autoimmune disease creates antibodies that may annul neutrophils and create neutropenia. Enlarged spleen patients also have little neutrophils due to enlarged spleen that catches and abolish neutrophils.
There is a really complicated disorder aplastic anemia that cuts down productions of neutrophils. This disorder stops bone marrow function. Neutrophils may be decreased with several inherited diseases as well. Also patients with viral influenza, cancer, tuberculosis, lack of vitamin B12, myelofibrosis, or deficiency of folic acid or patients who have had radiation therapy may develop neutropenia due to a limited production of neutrophils in bone marrow.
Medications that are not to be taken in case of diagnosed neutropenia and that can reduce bone marrow’s ability to create neutrophils are;
Dilatin, ChloramphenicolSulfa drugsChemotherapy drugs Benzene and insecticides drugsSymptoms
There are acute neutropenia and chronic neutropenia. The acute one may develop in a few hours and chronic one develops gradually in months. But there are no specific symptoms for neutropenia and it gets to be diagnosed only when infection develops. Acute neutropenia causes fever and ulcers around anus or mouth that might be very painful, which are coming before possible bacterial pneumonia or some other bad infections. While chronic neutropenia is lighter disorder, where neutrophils are very low in numbers and develop intermittently: it is called cyclic neutropenia.
Treatment
With neutropenia damaged bone marrow may recover on its own. But viral infections may resolve after the infection treatment. While mild neutropenia do not need treatment at all, severe neutropenia patients have no bodies to fight infections and are primarily treated with antibiotics, no matter of all other necessary details to be diagnosed. In general, first sign of neutropenia is fever.
For instance, neutropenia developed due to an autoimmune reaction may be treated with corticosteroids. An aplastic anemia neutropenia requires antithymocyte globulin or similar type of therapy. The neutropenia due to hypersplenism needs removing of enlarged spleen. And tuberculosis or leukaemia caused neutropenia may need a bone marrow/stem cell transplantation.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...