
Whooping cough, medically known as pertusis, is a serious and very contagious disease caused by Bordetella pertussis. Bordetella pertussis is a bacterium that affects the respiratory tract and leads to its inflammation. The disease may last up to 6 weeks and its name is related to a 'whoop' sound which is produced during inspiration after the attack of cough. The specific sound may be absent in babies since they are not strong enough to produce it.
Presentation of Whooping Cough in Infants
The infection generally starts with cold or flu-like symptoms such as runny nose, sneezing. Cough is in the beginning mild. This mild cough lingers for a couple of weeks and then becomes more severe and in a 'whooping' form. Infection is in majority of cases accompanied by fever. A characteristic cough features with coughing for 20-30 seconds and what follows is struggle for breath before the next coughing spell occurs. Coughing episodes are more frequent at night. The child may be seriously deprived of oxygen which results in peripheral cyanosis. The coughing attack may also end up with vomiting thick mucus.
Whooping cough can be very dangerous condition for children under the age of 1. The risk of complications is increased in all children who are prone to pneumonia, convulsions etc.
How does the Infection Occurs?
Whooping cough is a highly contagious illness. It can be transferred via droplets (coughing and sneezing) or direct contact with an infected person. The bacteria enter the body through the nasal or oral cavity. In many countries children are routinely vaccinated against whooping cough and the vaccine is given as a part of DTaP series. The vaccination starts when a child turns 2 months and ends between 4 and 6 years of age. It is highly effective in prevention of whooping cough.
Treatment for Whooping Cough in Infants
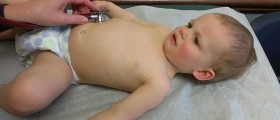
The doctor investigates a child's medical history and performs thorough physical examination. It is essential to auscultate child's lungs. In case the doctor suspects on whooping cough he/ she prescribes specific medications (appropriate antibiotics) which will eradicate infective agents even prior receiving laboratory results which confirm the infection caused by Bordetella pertussis.
The child is supposed to be isolated from other people and this way further spread of infective agents can be successfully prevented. Once the symptoms and signs subside (approximately after 6-10 weeks) people from the surrounding are safe.
Parents are due to follow doctor's orders and never give their child any medication without previous consultation. This way they may cause aggravation of the symptoms and induce certain complications.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...