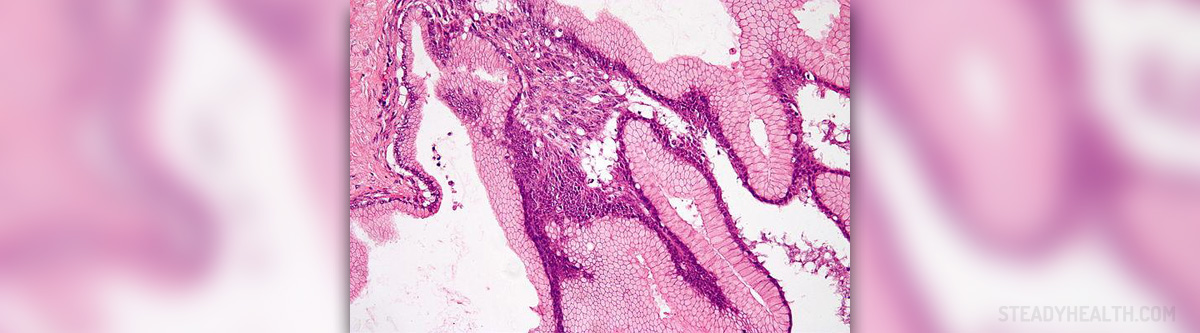
Glioma is a tumor of brain tissue, to be more precise tumor originating from specific brain cells called astrocytes. Low grade glioma is a benign tumor. Stage I and II gliomas are considered low grade tumors. The most common type of gliomas are astrocytomas and even they can be further classified into pilocytic, pilomyxoid and fibrillary astrocytomas. It is estimated that around 80% of astrocytomas affecting children are actually low grade tumors.
The main characteristic of these tumors is their slow progression. Astrocytomas may affect each and every part of the brain or the spinal cord. However, the common location of tumor growth includes the cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum. The tumor is either solid or cystic (filled with fluid).
Low Grade Glioma Incidence
Low grade glioma represent the most frequent type of brain tumor in children. It accounts for up to 40% of all childhood brain and spinal cord tumors. Still, the tumor may also affect adults. It is not clear why gliomas occur. What is confirmed is that low grade gliomas are associated with neurofibromatosis type 1, one of many genetic conditions.Low Grade Glioma Clinical Characteristics
Symptoms and signs of low grade glioma practically depend on tumor location, its size and whether the pressure inside the skull is increased or remains unchanged.
Increase of intracranial pressure is commonly associated with nausea, vomiting and prolonged or repeated headaches of different intensity. Furthermore, patients may be lethargic or irritated, clumsy with noticeable personality or behavioral changes. The affected children may show gradual decline in school work or have difficulty regarding different tasks such as handwriting. The tumor may affect child's walk and cause abnormal gait. The spread of the tumor to the spinal cord is associated with back pain, difficulty walking and inadequate bladder/bowel control.
Diagnosing Low Grade Glioma
While investigating the tumor it is essential to get more information about its type, position and size. This way doctors can opt for the most convenient treatment.
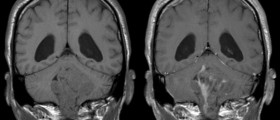
CT scan and MRI are very helpful when it comes to determining tumor size and its location. In some cases these imaging methods may also help in diagnosing the very type of tumor. They perfectly visualize the tumor and are also used in further evaluation of treatment and progression or improvement of the disease.Low Grade Glioma Treatment
Treatment for low grade glioma generally depends on tumor location and patient's age.
Many children require surgery which confirms the diagnosis and also alleviates symptoms such as increased intracranial pressure and associated problems. The goal of the surgery is to completely remove the tumor or to reduce its size as much as possible. Unfortunately, not all tumors are operable. In such case, if it is possible, a surgeon performs tumor biopsy. Sometimes even biopsy cannot be performed and such patients undergo other treatment modalities.
Radiotherapy is generally performed after surgical removal of glioma and it is also indicated in inoperable patients. Some patients are treated with chemotherapy, which is administered either alone or in a combination with radiotherapy or surgery.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...