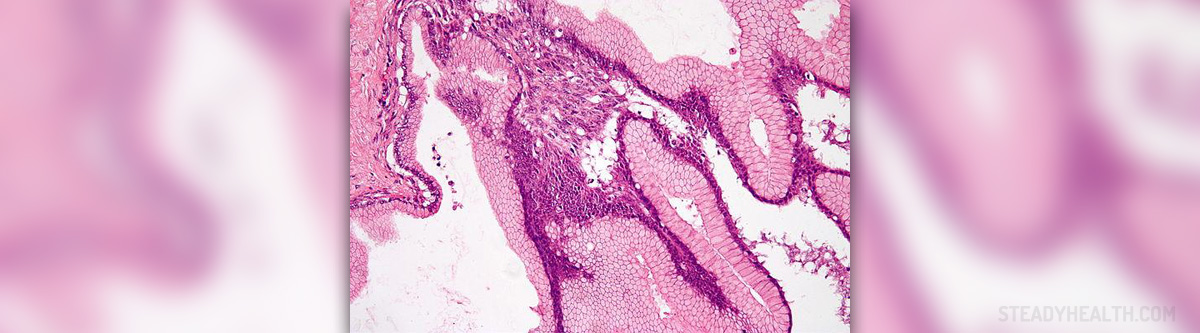
There are many laryngeal lesions that can be classified as benign laryngeal tumors. Most of them cause hoarseness, changes in voice quality and stridor. Dysphagia is another potential problem of certain laryngeal lesions.
Out of numerous laryngeal lesions vocal cord nodules, cystic laryngeal lesions and recurrent respiratory papillomatis are the most common ones.
Vocal Cord Nodules
Vocal cord nodules are benign growths typically affecting the medial aspect of the vocal cords. They may develop on one vocal cord or bilaterally. The very presence of vocal cord nodules is associated with hoarseness and changes in voice quality. The condition predominantly affects women and is frequent between the age of 20 and 40.
In majority of cases vocal cord nodules develop as a result of vocal abuse and vocal overuse. The condition also affects people suffering from laryngopharyngeal reflux.
Diagnosis can be easily confirmed thanks to patient's history of persistent hoarseness, changes in voice quality and after visualization of the nodules. Proper insight in the vocal cords and nodules is achieved with fiberoptic exam and videostrobolaryngoscopy.
Treatment for vocal cord nodules includes voice therapy, education and surgery. Laryngopharynegal reflux also needs to be brought under control.
Vocal Cord Cystic Lesions
Vocal cords can be affected by two types of cysts, mucus retention cysts and epidermoid cysts. Mucus retention cysts, as the name suggests, contain mucus which accumulates due to blockage of mucus-producing glands and epidermoid cysts contain keratin debris.
Similarly to other laryngeal lesions, both of the mentioned cysts are associated with hoarseness, changes in voice quality and vocal strain.
Diagnosis is confirmed with fiberoptic laryngoscopy and videostroboscopy while treatment initially includes voice therapy and only in case it is ineffective, patients undergo surgery. One more conservative treatment for vocal cord cysts includes steroids.
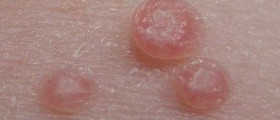
Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis
It is estimated that recurrent respiratory papillomatosis is the most common benign laryngeal lesion. The condition is also the second most common cause of hoarseness. It is characterized by multiple exophytic lesions that occur all the way down the airway.
Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis may have adult or juvenile onset. Interestingly enough, juvenile form of the disease resolves by puberty. This medical condition is closely related to Human papilloma virus (HPV) serotypes 6 and 11.
Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis is treated surgically. The goals of the surgery are reduction of tumor burden and improvement of voice quality. It is also important to establish a safe airway and minimize the spread of surgery as well as extend the interval between surgical procedures.





-And-Breathing-Problems_f_280x120.jpg)





Your thoughts on this
Loading...