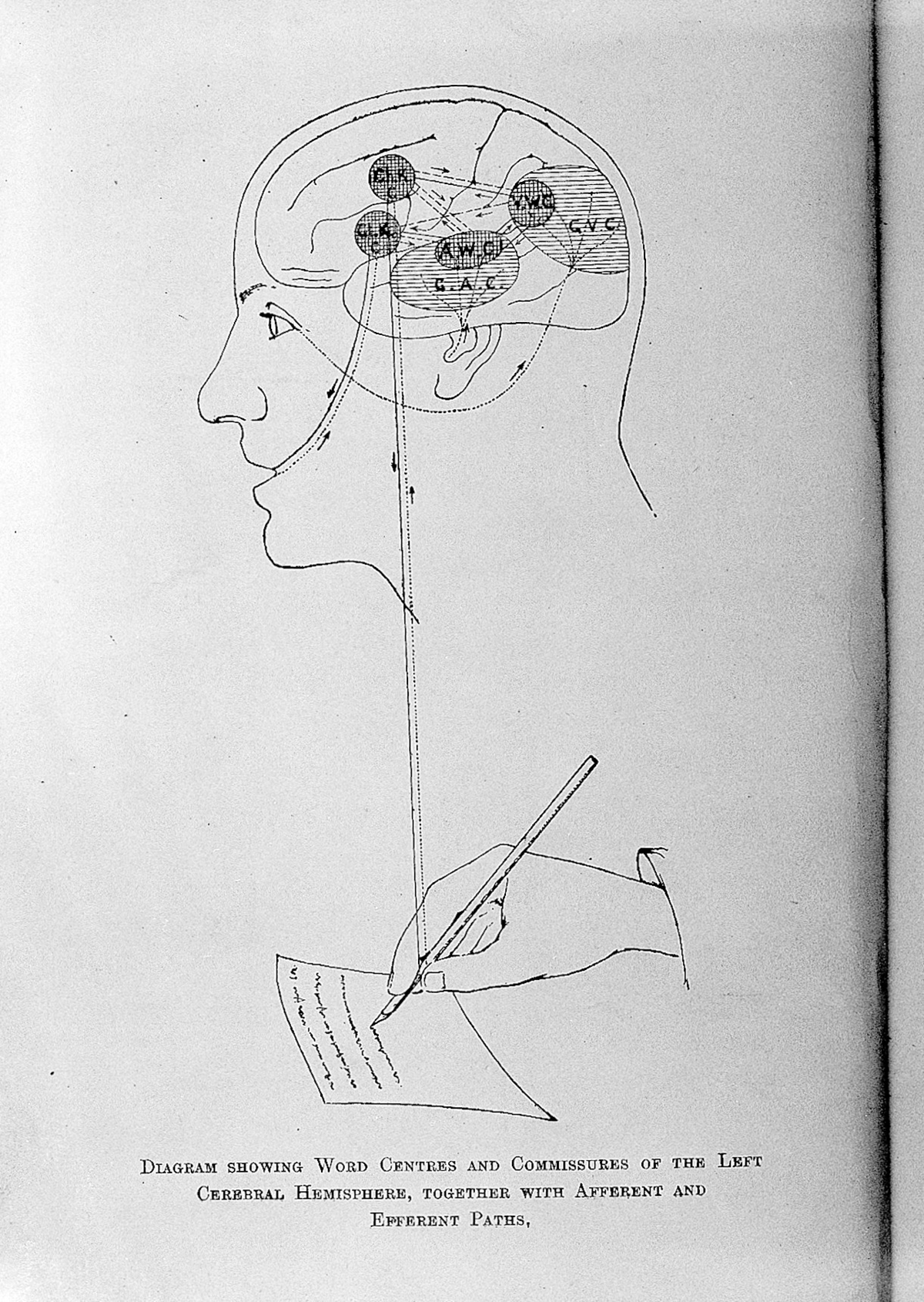
What is Aphasia?Aphasia is a disorder that results from damage to the part of the brain that is responsible for language. Left hemisphere of brain controls language and aphasia usually occurs due to some injury to that portion of the brain. Language enables us to use words, read, write, listen, express our thoughts and recognize other people’s words. Aphasia impairs these abilities. Severity of aphasia depends on location and extent of the brain damage and may even have tragic consequences. This neurological disorder is sometimes accompanied with other speech disorders like dysarthria or apraxia of speech, caused by damage to the brain as well. Aphasia can affect people of all age though it is commonly seen in adults who have had a stroke. Both males and females can suffer from the condition. Aphasia may occur abruptly after a head injury or a stroke and it may develop gradually due to brain tumor or certain degenerative disease. It has been estimated that around 1 million Americans suffer from aphasia and approximately 80,000 people get affected by the condition after a stroke every year.
Causes and Symptoms of Aphasia
As already mentioned, aphasia is caused by damage to the portion of the brain that controls language. In most cases it results from a stroke that is due to disruption of the blood supply to the brain. This leads to brain cell death because of lack of oxygen and vital nutrients. Aphasia can be also due to head injury, brain tumor, an infection of the brain or dementia. A person with aphasia may speak using only nouns and verbs, use incorrect words, not comprehend words, make spelling errors, have difficulty working with numbers and generally have difficulty communicating.
Types of AphasiaThree most common types of aphasia include:
Wernicke’s Aphasia
Wernicke’s aphasia is associated with serious comprehension difficulties. People with this type of aphasia cannot understand others and commonly speak incomprehensible. Their words are often arranged randomly. However, they are usually unaware of their language impairment.
Broca’s AphasiaThis type of aphasia occurs due to injury to the left frontal area of the brain. People with Broca’s aphasia have difficulty forming complete sentence, usually speak in short sentence and leave out words. They may understand what others are saying to some degree and they are often aware of their own difficulty in communicating.
Global Aphasia
Global aphasia results from severe and extensive damage to the brain. People with global aphasia usually loose almost all language function, both comprehension and expression. They have difficulty forming sentences and speaking and difficulty understanding spoken language.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...