Peripheral artery disease
The circulatory system is one of the most important systems in the human body. It is comprised of the heart, the blood vessels and the blood. Many people usually pay attention only to the heart and the large arteries that are above the heart, such as coronary arteries that supply the heart with blood and carotid arteries that supply the brain with blood. Therefore, the blood vessels below the heart, which are called peripheral arteries, are usually neglected. However, these peripheral arteries supply the kidneys, intestines, arms and legs, and may also be affected by certain disorder. Peripheral artery disease occurs when the peripheral arteries are blocked or narrowed due to the formation of the plaque of the accumulated cholesterol and fatty materials.
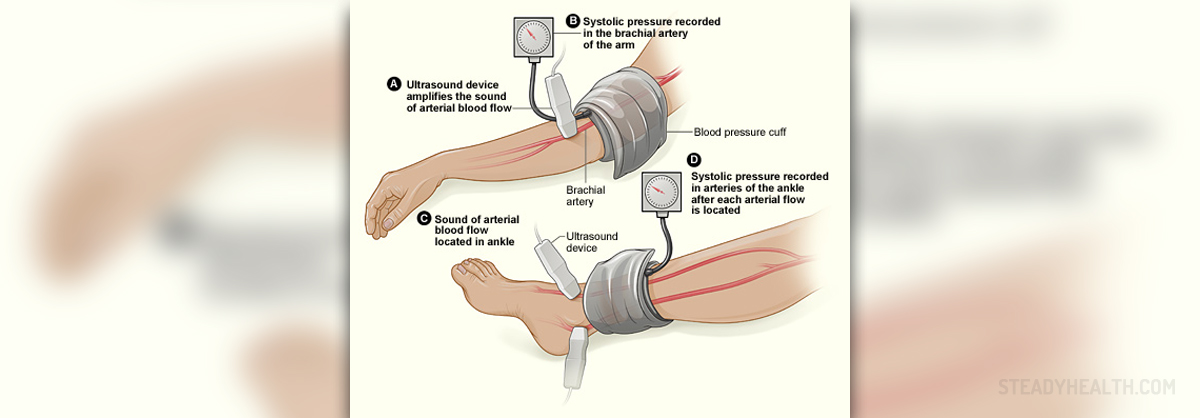
Ankle-brachial index
Ankle-brachial index is a blood test when certain problem occurs in the peripheral arteries. The blood pressure is normally measured at the brachial artery in the crook of the arm. However, when there is a blockage somewhere in the peripheral arteries, then the pressure at places that are further from the heart can differ from that in the arm. The ankle-brachial index evaluates blood pressure from two places. When there is a large difference between the two blood pressures, that it indicates the presence of peripheral artery disease.
When a person notices some symptoms of peripheral artery disease, such as pain or cramping in the calves, thighs, hips or buttocks, as well as slow-healing wounds on the toes, feet or legs, he/she should have an ankle-brachial index test. People, who are smokers, or those who have diabetes, suffer from hypertension or high cholesterol is at high risk to develop peripheral artery disease. Since this disease sometimes does not show any signs, it is important for people who are at risk to take an ankle-brachial index test. This test lasts about fifteen minutes at most and no special preparation is necessary. The ankle-brachial index is obtained when the highest pressure at the ankle is divided by the highest pressure at the brachialartery.
Normal level of ankle-brachial index
It is considered that the normal level of ankle-brachial index ranges from 0.90 to 1.30. When the level of ankle-brachial index is under 0.90, it means that the blood has difficulty to normally flow to the legs and feet. The index from 0.41 to 0.90 represents mild to moderate peripheral artery disease, while the index 0.40 and lower represents severe disease. When the ankle-brachial index is over 1.30, it usually indicates stiff, calcium-encrusted arteries.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...