Peripheral artery disease is a term that refers to a common circulatory problem which develops due to narrowing of the arteries and insufficient blood supply of certain tissues.
In people suffering from peripheral artery disease specific changes predominantly affect the arteries of the legs. The most prominent symptom of the condition is leg pain that occurs during walking (medically known as intermittent clausication). In majority of cases peripheral artery disease is associated with generalized atherosclerosis in which fat deposits accumulate inside many blood vessels and cause serious narrowing. Such patients apart from problems with circulation of the peripheral organs (limbs) are also at a higher risk for even more serious illnesses such as heart attack and stroke.
What are Clinical Characteristics of Peripheral Artery Disease?
Many patients suffering from peripheral artery disease have either no symptoms or they complain about mild symptoms and signs. The most commonly reported problem is pain in the legs associated with walking (intermittent claudication). This pain (or cramping) is always triggered by some activity and tends to disappear after a few minutes and always subsides with rest. The actual location of pain depends on the location of blood vessel narrowing. The pain varies in intensity and is sometimes simply unbearable.
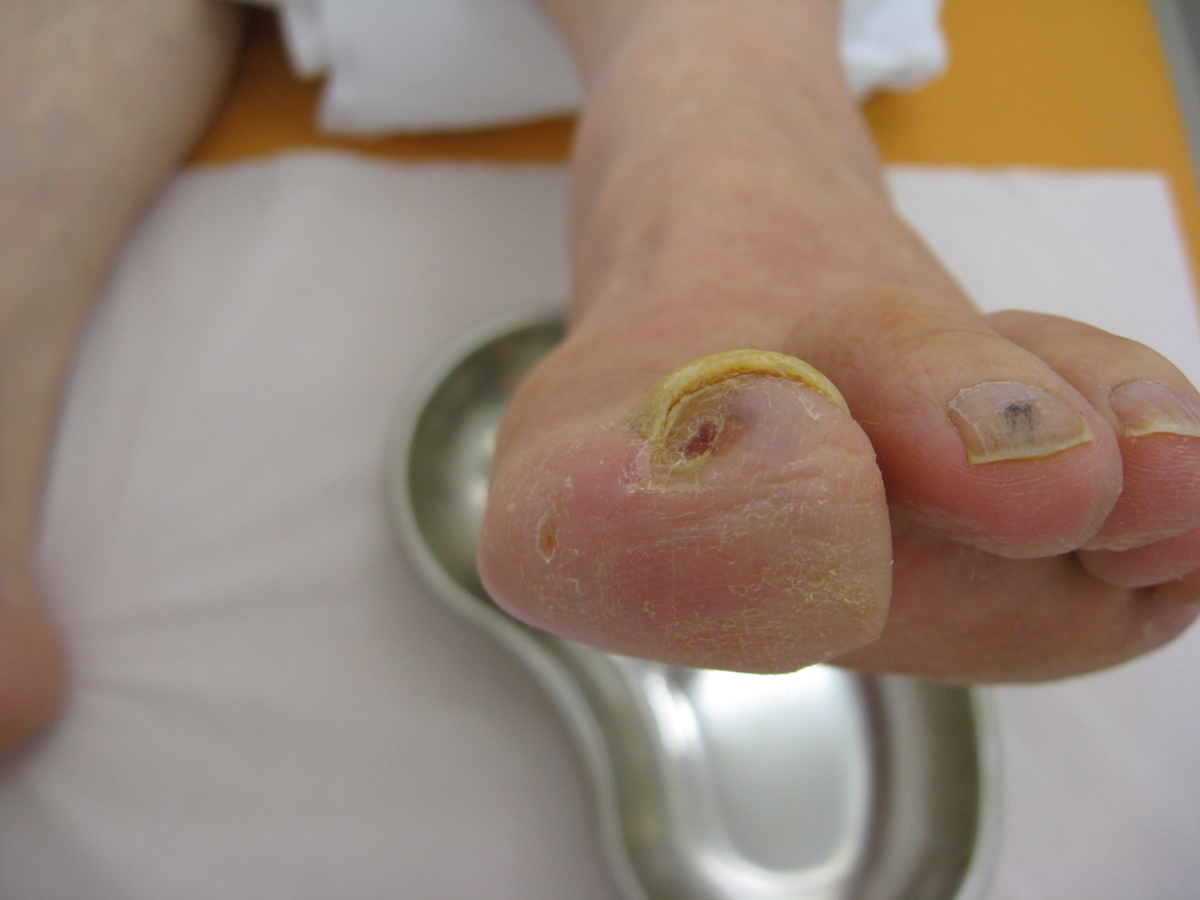
Apart from pain/ cramping in lower extremities patients suffering from peripheral artery disease additionally complain about leg numbness or weakness and coldness of the lower leg or foot (particularly if the temperature of the affected leg is compared with the temperature of the healthy leg). In severe cases there are sores that simply do not heal. In some people there is also loss of hair in the parts that are supplied with the narrowed artery. The growth of nails can be slower on the affected foot and there is also a difference of the pulse felt on arteries of the healthy and the affected leg. Men suffering from peripheral artery disease may additionally suffer from erectile dysfunction.
Causes and Risks of Peripheral Artery Disease
The condition generally develops due to the process of atherosclerosis. Even though atherosclerosis predominantly affects heart vessels and vessels in the brain, there is also possibility that the arteries of the extremities (particularly the lower ones) will become affected. Apart from atherosclerosis peripheral artery disease is associated with inflammation of blood vessels, injury to the limbs, abnormal anatomy of the ligaments and muscles in the legs and the condition may occur as a consequence of radiation exposure.
The risk for peripheral artery disease is increased in patients suffering from diabetes, obesity, high cholesterol levels and high blood pressure. Furthermore, the disease is more frequent among smokers and older adults (people above the age of 50) as well as among people with a family history of peripheral artery disease, heart attack or stroke.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...