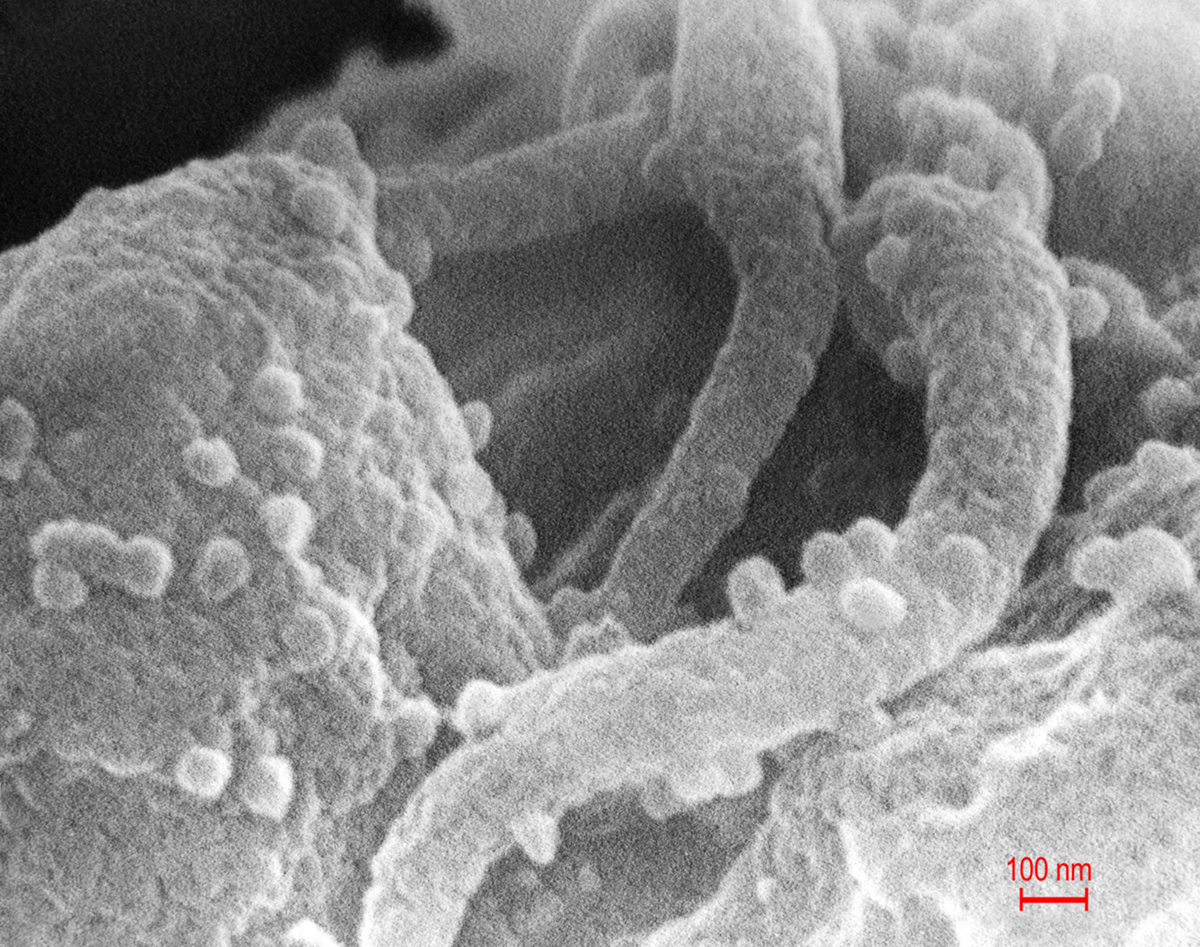
HIV seroconversion
Seroconversion explains the process of the response of the immune system of the body to certain infection or immunization. In the case when a foreign body such as virus, bacteria, toxins, enters the organism, the immune system of the body detects it and begins to produce the white blood cells or antibodies that have the role to fight against the foreign bodies or antigens. Seroconversion is the name for the process of producing these antibodies to a specific antigen. When a person with HIV has HIV antibodies that are noticeable in blood test, in that case that person is regarded as seropositive.
Acute infection phase
The acute infection phase is a period between about two weeks and three months after the person was exposed to HIV. The acute infection phase is the period when seroconversion occurs. The immune system of the body detects the HIV virus and subsequently creates antibodies to fight the virus. However, because the immune symptoms becomes overwhelmed, certain physical symptoms appear during this period. If a person cannot treat the symptoms alone, it is necessary to take medical care or even to be hospitalized. At the end of the acute infection phase, the immune system produces enough antibodies and a positive HIV antibody test results in the HIV infection diagnosis.
Symptoms of HIV seroconversion
The most common symptoms of acute HIV infection or HIV seroconversion are very much like those symptoms that are characteristic for the flu and mononucleosis. A person who suffers from this infection may feel pain in the muscles. Furthermore, he/she is constantly tired and exhausted. Fever and headache may also appear in the person with HIV seroconversion. Many patients may experience nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, while in some cases the common symptoms are sore throat, mouth ulcers and the skin rash. In the majority of cases with acute HIV infection, the patient has the swollen lymph nodes, which occurs as a consequence of the body’s immune response to the introduction of HIV
Diagnosing seroconversion
The most reliable test for the diagnosing acute HIV infection is a blood test, which must be done again six months after exposure to HIV. However, it is very important that every person does the blood test once a year, in order to be sure that is not affected by this serious disease. In the case, when the HIV infection is discovered in the acute infection phase, it should be immediately treated with anti-retroviral therapy.






_f_280x120.jpg)


Your thoughts on this
Loading...