
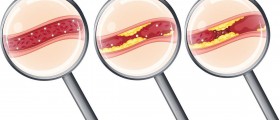
Acute coronary syndrome is generally associated with atherosclerotic plaque rupture and partial or complete thrombosis in the infarct-related artery. Plaque rupture is often caused by the dissolution of the fibrous cap and the subsequent release of metalloproteinases. However, stable coronary artery disease can also lead to acute coronary syndrome in the case of the occurrence of physiologic stress. In a wider context, the term applies to a variety of clinical conditions.
Causes
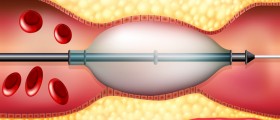
As indicated, most cases of Acute coronary syndrome occur as a result of plaque rupture. Rupture and metalloproteinases release is followed by platelet activation and aggregation, Vasoconstriction and activation of the coagulation pathway. Distal embolization might occur in addition to intraluminal thrombosis and vascular occlusion.
Outlook
Outlook for the patient will depend on the severity of the arterial obstruction, stress on the heart and the compensative qualities of the heart. About thirteen per cent of those with NSTEMI ACS fell into a six-month mortality rate category. The figure is eight per cent for those with unstable angina. Those who suffer from coronary disease often suffer also from testosterone deficiency, which can lead to increased risks with regard to mortality. Those with a previous history of heart failure, renal failure, dementia and peripheral artery disease are of course more vulnerable to mortality as a result of this condition. For those with comorbid conditions, the risk was greatest during the first weeks after the occurrence of NSTEMI ACS.
Treatment and recovery
With regard to treatment and recovery, it is important that patients be properly educated with regard to the risks they might face as a result of the occurrence of the condition. If a patient fails to recognize or identify his or her symptoms, this can be problematic in terms of recovery and rehabilitation, as well as delays in the time that it takes for a patient to seek medical attention. Patients should be advised to quit smoking and be aware of the dangers of this activity. The risk of a coronary event recurring decreases by half after a year without smoking. Thus, smokers should be provided with education, guidance and support with regard to kicking the habit. It might also be advisable for smokers to attend classes that will help them to avoid smoking after myocardial infarct.
Diet also plays an important role in the avoidance of CAD. Patients should thus be evaluated and advised by a dietician. Low cholesterol, low salt diets should be advised.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...