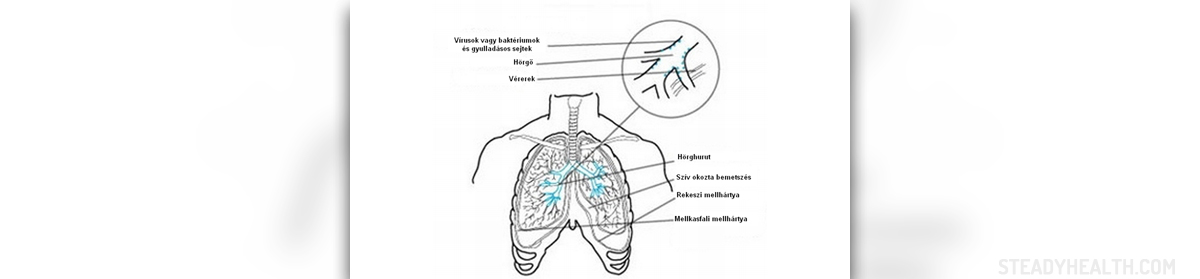
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the main air passages in the lungs and it can develop in acute or chronic form. Acute bronchitis is in many cases caused by viruses.
Clinical Characteristics of Acute Bronchitis
Symptoms of acute bronchitis develop 3-4 days after the onset of infection of the upper respiratory system (cold, flu etc.). A person develops cough which is actually the leading symptom of acute bronchitis. Cough is initially dry and only after a few days the person starts to cough up mucus (clear, yellow or green). In some cases mucus may contain small streaks of blood.
The person also suffers from mild fever (basically less than 101F). In case of higher body temperature one is highly likely to develop pneumonia. Additional symptoms and signs of acute bronchitis include a general feeling of tiredness, sensation of tightness, burning and dull pain in the chest, whistling noises when breathing and hoarseness.
In majority of cases patients fully recover after 2-3 weeks while up to 20% of people may cough for up to 4 weeks.
Treatment for Acute Bronchitis
The goal of the treatment for acute bronchitis is to take care of cough, fever and pain. Medications such as antibiotics are not generally recommended since they are simply ineffective against viruses. In people who are already suffering from other lung conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma or those with heart failure the treatment is a bit more complex.
A person suffering from acute bronchitis is supposed to drink a lot of fluids, use cough drops and avoid any type of lung irritants (particularly cigarettes). Depending on the type of cough patients are either prescribed cough suppressants or expectorants. Children under the age of 2 are not supposed to be given cough and cold medicines until the doctor is consulted. Caffeine and alcohol must not be consumed during illness since they can induce dehydration.
It is essential for a patient to have plenty of rest and this way obtain optimal level of energy to get better. Fever and body aches are successfully relieved with acetaminophen, ibuprofen and similar medications.
Breathing difficulties are eased with a humidifier and hot shower. The heat and moisture make mucus more moist and make coughing-up easier.
Prescribed medications that may be administered in people suffering from acute bronchitis include inhaled beta 2-agonists. They dilate the airways allowing more air to enter the lungs. They help people with breathing difficulties. An finally, only in people who are at increased risk administration of antibiotics can be justified.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...