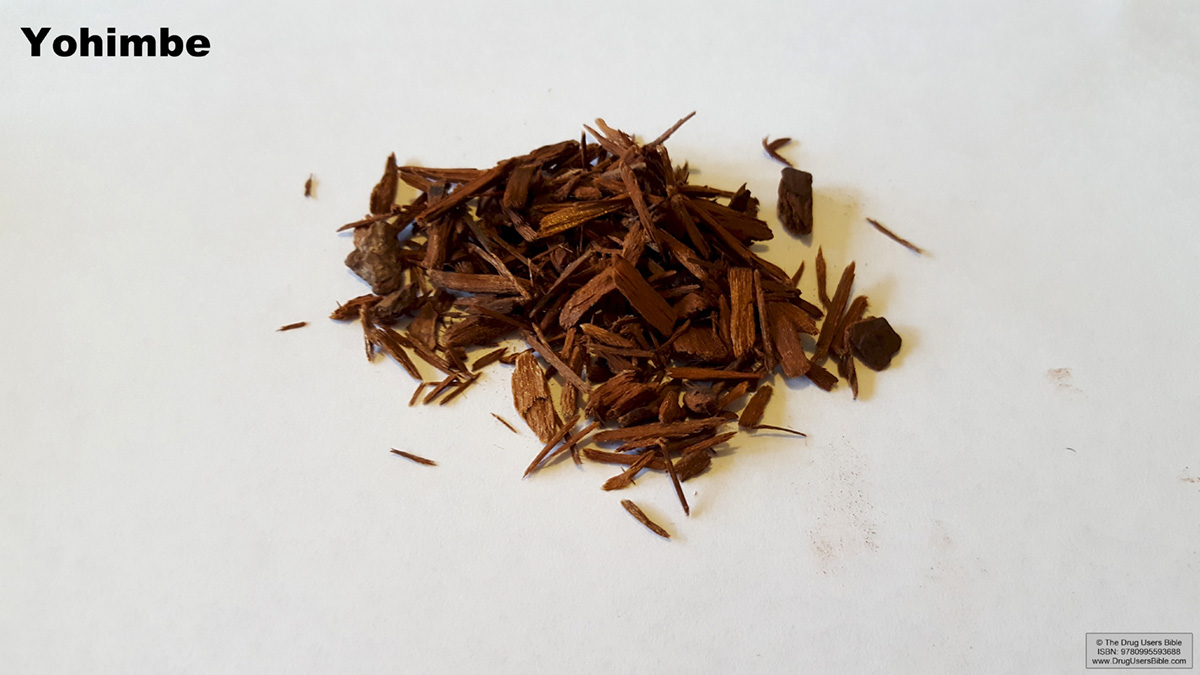

The Yohimbe tree and its bark
Yohimbe is a tree whose bark has been utilized for centuries to enhance sexual ability and treat angina and hypertension. It is mostly found in countries like Cameroon, Zaire and Gabon, and it is used in medicine nowadays to treat impotence, as well as to increase the blood flow to the male and female genitals.
The bark is obtained in the time period between May and September, because, at this time, the trees contain the highest amount of alkaloid and should be garnered then. Another tree is commonly planted as the harvested tree dies after the bark extraction process.
Benefits and negative side effects of Yohimbe tree bark
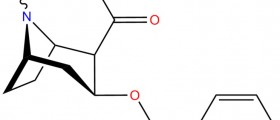
An indole alkaloid called Yohimbine is the primary chemical contained inside the bark. Due to its ability to expand blood vessels, Yohimbine can prevent certain depression related disorders. Its other abilities include inhibiting a sympathetic nervous system component called the alpha-2 adrenergic receptors, as well as heightening the temperature of the body and bolstering the heart rate.
Fatigue, stress and tension related impotency can be avoided by utilizing the yohimbe bark due to the chemical reaction it induces, which can also aid diabetics and heart disease patients. The bark can boost adrenaline supply to the nerve endings and thus cause faster sensual stimulation in men, and is also known to lower the blood vessel constricting hormonal effect of the alpha-adrenoreceptor.
Yohimbe bark should not be utilized with food items such as aged meats, chocolate, beer, cheese and nuts, as they contain large amounts of tyramines. Avoiding any product containing phenylalanine, tyramine, tyroscine and amino acids is advised when consuming yohimbe bark. Due to the monoamine oxidase in the bark being able to heighten the blood pressure, it is not recommended to persons that suffer from high blood pressure. The bark can be prepared in tea form, but should never be consumed in excessive amounts.
Its negative side effects involve agitation, insomnia, skin flushing, rash, tremors, nausea, nervousness, painful urination, increased salivation, headache, dizziness, anxiety, irritability, runny nose, muscle aches, kidney failure, insomnia, frequent urination, diarrhea, vomiting, cough, breathing difficulties and a reduced appetite. Consumption in large amounts has been shown to heighten seizure and motor activity. Retention of body fluids, which can lead to a discomfort in the chest and heart rate increase has also been observed. The bark should be avoided during pregnancy, as its uterus relaxing properties can lead to damage caused to the fetus. Ingesting the bark during breast feeding is also not advised.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...