
Hearing impairment is one of the most frequent disabilities affecting people of all ages. It is divided into congenital (present at birth) or acquired (affecting individuals who have been able to hear but suddenly lost the ability). The condition is easily diagnosed with several tests and exams. It is essential to diagnose hearing loss as soon as possible and start with the most suitable treatment.
Newborn Hearing Screening Programme
Newborn hearing screening programme (NHSP) is a way of diagnosing hearing loss in babies soon after they are born. This testing is highly suitable because babies cannot willingly participate and cannot tell whether they can hear sounds or not.
After the baby is born, he/she undergoes many routine health exams and tests, one of which is a hearing test. The test is a part of NHSP and is basically performed within several weeks after the child is born.
The otoacoustic emissions (OAE) test is performed in majority of cases and preferably while the child is asleep. Testing consists of inserting a tiny probe in the child's ear. The probe sends sounds and also checks for a responding echo originating from the ear. This 'echo' is actually an otoacoustic emission. In case while testing there is no reported response, this may suggest hearing impairment, although definitive conformation can be achieved only after performing additional tests.
Adult Hearing Tests
Older children as well as adults who are likely to have developed hearing loss of various degree undergo specialized exams and a tests which confirm hearing loss, determine the type of the disease and the degree of damage to the auditory system.
After asking a standardized set of questions, doctors continue with ear examination, tuning fork test, audiometry test and bone oscillator test.
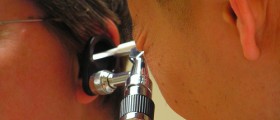
During the ear examination (performed with the assistance of an otoscope) doctor can detect discharge coming from the outer ear, a bulging ear drum, perforated ear drum or blockage caused by fluid or some foreign object.
Tuning fork test is performed by ENT (ear, throat and nose) specialist. Tests includes placing of a tuning fork (a Y-shaped metallic object) onto the patient's ear. The test allows the doctor to have insight in whether the sound is transmitted through air vibrations to the inner ear. It is also possible to place a tuning fork onto the bone behind the ear this way testing transmission of sound waves via the bone.
Audiometry test is performed with earphones attached to a specific machine. The patient is exposed to different tones and volumes and is supposed to confirm when the sound is heard. Conformation is achieved either by raising one's hand or pressing a button. This test may also check whether a person understands words spoken at different volumes. So, patients are due to repeat the particular word after it has been spoken at different volumes.
Finally, bone oscillatory test is performed to check transmission through the bone. Similarly to the tuning fork test, patients are tested by placing an instrument called a bone oscillator against the bone behind the ear.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...