Loss of hearing may be provoked by many things, including different injuries, diseases and genetic defects, as well as exposure to loud sounds. On the other hand, some people may experience temporary deafness due to the use of some drugs (such as chloroquine or antibiotics aminoglycosides), infections or because of the accumulated ear wax. Foreign objects in the ear canal could also be the reason behind hearing loss.
Deafness Types
There are several different ways to categorize deafness. As mentioned, it can be temporary or permanent condition, depending on the duration of the symptoms. Some of the types of deafness include: conductive, nerve as well as congenital and adventitious deafness.
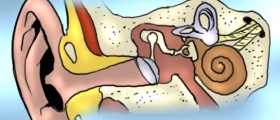
Conductive deafness is usually caused by problems in the bones of the middle ear (hammer bone, anvil bone or stirrup bone). Because of that, the sound waves can’t pass to the inner ear. Additionally, eardrum might not vibrate to respond to sound waves coming to the ear and the person can’t hear. Conductive hearing loss may be associated with accumulated fluid in the ear, but this condition can be treated and most patients regain normal hearing after that.
Traumas, diseases or some other events affecting the cochlear nerve are known to cause nerve deafness. In people suffering from this problem, there are no electrical impulses coming to the brain and that’s why they lack the hearing. This hearing problem is not treatable.
Congenital deafness is loss of hearing present from the birth, while all other cases of loss of hearing are known as adventitious deafness.
Congenital Deafness
Hereditary disorders might be the cause of hearing loss present since the birth of a child. Parents passed certain flawed genes to their child and he or she can’t hear because of that. In most patients diagnosed with this hearing loss, the problem is caused by malformations of the structure of the inner ear.
Exposure to some diseases may also lead to hearing problems or deafness in unborn children. If the pregnant woman was exposed to influenza, mumps or rubella (German measles) there are increased chances the baby will be born with some hearing difficulties. Exposure to quinine or to methyl mercury may also lead to deafness in utero.
Genetic disorders are yet another factor which may contribute to development of hearing loss in unborn kids. Trisomy 13 S, multiple lentigines syndrome, as well as osteogenesis imperfecta are some of genetic problems known to be associated with deafness.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...