
Albinism Overview
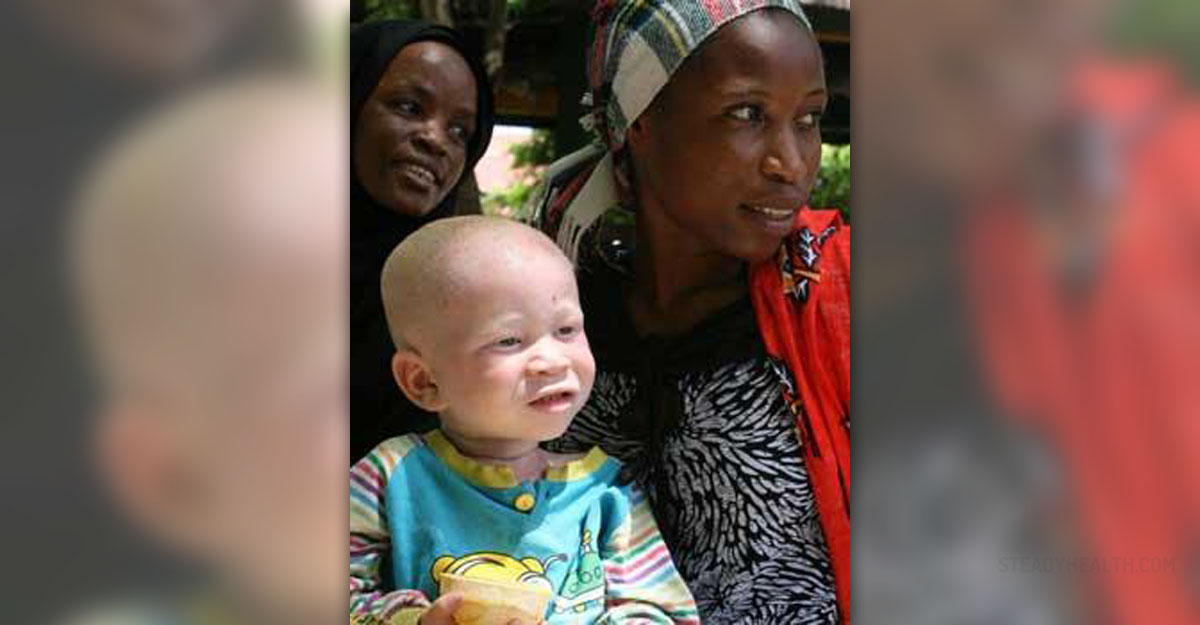
Albinism is a condition characterized by absence or insufficient production of the pigment in the skin, eyes and hair. This genetic disease is caused by inability of the body to produce or distribute the pigment known as melanin which colors the iris of the eye, skin and hair. Melanin, naturally occurring chemical in the body, also has a role of protecting the skin from ultraviolet rays of the sun and is important in normal development of vision.
There are different types of albinism and they are all caused by genetic abnormality that results in poor production of melanin in the body. Albinism is usually passed on through family and occurs in individuals who inherit mutated genes from each parent. On the other hand, an individual who gets albinism gene from only one parent will be only a carrier of the disorder but will not be affected.
Symptoms of Albinism
There are two main forms of albinism, oculocutaneous albinism and ocular albinism. Oculocutaneous albinism causes vision problems and light or pale color of the skin, hair and eyes. In some individuals with albinism the skin pigmentation never changes whilst in others production of melanin may start or increase during childhood or adolescence resulting in pigmentation changes.
With exposure to the sun, those suffering from oculocutaneous albinism, may develop freckles and moles on the skin. Also, they have the ability to tan. Hair in people with this type of albinism may range from white to brown although people of African or Asian descent may have yellow, red or brown hair color.
The eyes can vary from light blue to brown in color in people with albinism. However, eye color may change with age. The iris of the eye appears translucent due to the lack of pigment. Albinism causes the iris to look red due to inability to completely block the light from entering the eye. The disorder also affects the eye function and may cause astigmatism and nearsightedness or farsightedness. These vision problems are common for all types of albinism.
Ocular albinism affects only the eyes. Color of the skin and eyes are typically normal. However, eye examination reveals the lack of melanin pigment in the back of the eye (retina). Ocular albinism is featured by light sensitivity, also called photophobia. Rapid and involuntary back and forth movement of the eyes, a condition known as nystagmus, is also present. Finally, albinism is accompanied with crossed eyes (strabismus), the condition marked by misaligned eyes that are unable to point in the same direction.
Treatment for Albinism
Albinism can not be cured. The treatment for albinism is designed to relieve the symptoms. It mainly involves protecting the skin and eyes from the sun. Life long yearly checkups of the skin and eyes are necessary for people with albinism to prevent skin changes that may lead to cancer. Surgical treatment may be required to correct strabismus and reduce nystagmus.
People with albinism are advised to avoid exposure to sun in between 10 am and 4 pm. Prescription lenses are commonly given to improve vision while tinted glasses are needed to protect the eyes from the sunlight.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...