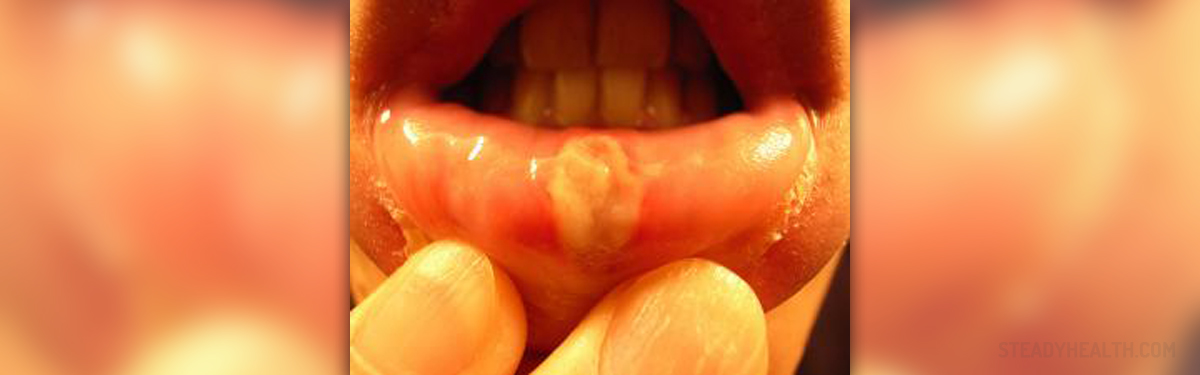
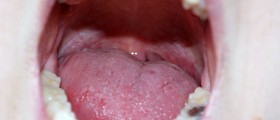
Stomatitis is an inflammatory condition characterized by localized inflammation of the mucous lining of any of the structures in the mouth: the cheeks, gums, tongue, lips, throat, and roof or floor of the mouth. This condition is especially common in children, where it is accompanied by fever, drooling and a generally uncomfortable feeling. The stomatitis, and resulting inflammation and ulcers, can be mild and localized or severe and widespread. Usually, the condition is very painful and may often hinder eating.
Causes of stomatitis
The stomatitis is caused by many different conditions. Sometimes, it results from a poor oral hygiene, deficiency of dietary protein, poorly fitted dentures, from various mouth burns from hot foods and drinks, from toxic plants, viruses or other health conditions. Viral stomatitis is usually caused by the herpes labialis virus, which also causes cold sores, which has a tendency to provoke the sores towards the front of the mouth, lips and tongue. Herpangina is another herpes related virus that may cause inflammation of the mouth region. The infection sometimes occurs due to recurrent aphtous stomatitis, other infectious agents such as Candida albicans and other bacteria, or as a side effect of chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Signs and symptoms of stomatitis
Stomatitis is usually accompanied by the inflammation and ulcers. The inflamed area is swollen and red. Painful ulcers usually appear on the swollen oral mucosa, usually more than one of them. In some rare cases mouth can appear normal, but the whitish lesions may form as the only symptom of inflammation. The sensation of burning pain in the mouth is also present. The affected area may bleed occasionally. If the blisters form in the mouth, they are often localized on the tongue, cheeks or at the roof of the mouth. The blisters pop and form ulcers, which are red and inflamed around the edges and have grayish white centers. The gums are also swollen, very irritated and may occasionally bleed. The patient usually has problems swallowing food and liquid and may complain about the foul-smelling breath.
Diagnosis and treatment
Stomatitis is usually diagnosed based on the appearance of inflammation. People should seek medical help if they experience problems with drinking and swallowing, high temperature and persistent symptoms that last more than three days. The treatment is carefully tailored to address the underlying cause of the stomatitis. Patients are advised to take very good and regular oral hygiene and avoid sharp edged foods. Local causes, such as sharp teeth or braces, are normally removed by a dentist or orthodontist.





_f_280x120.jpg)







Your thoughts on this
Loading...