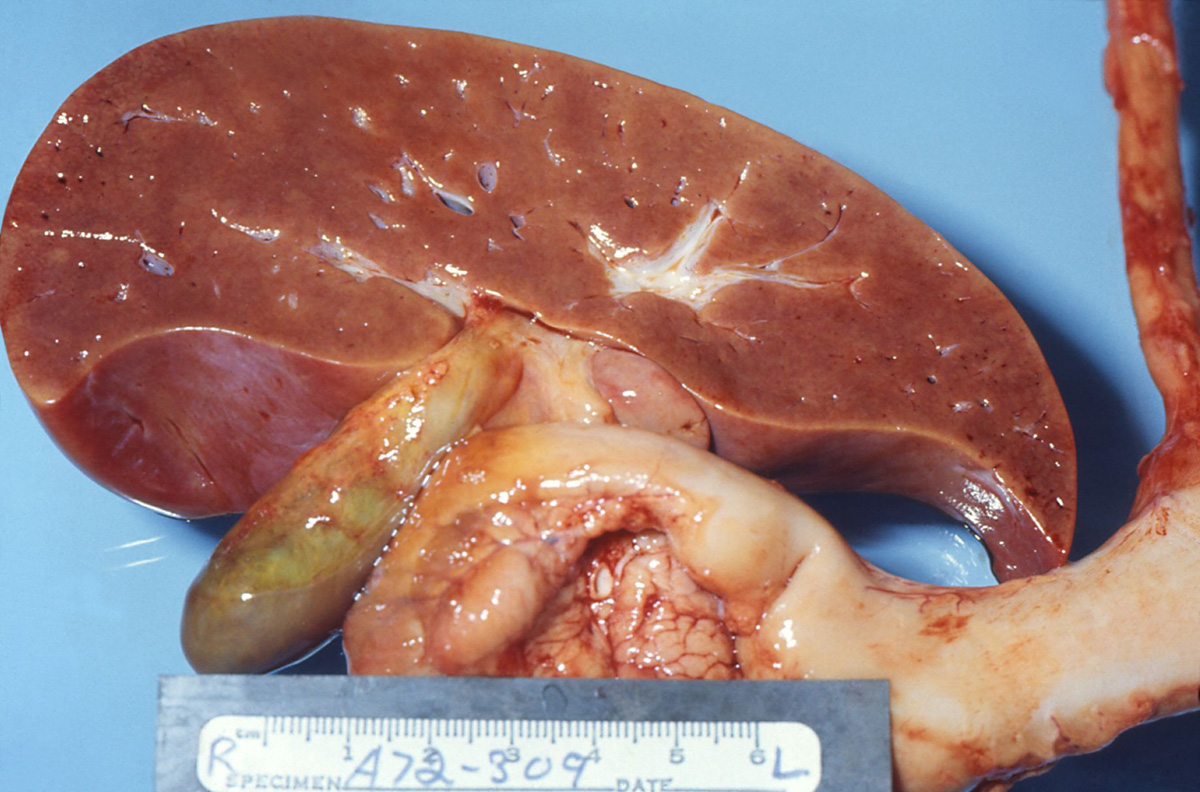
Reye's syndrome is a medical condition which affects children. It features with many detrimental effects to numerous organs and organs systems. The brain and the liver are most affected. The actual cause of Reye's syndrome has not been identified yet. However, the condition is related to Aspirin consumption in children suffering from viral infections. In some cases Reye's syndrome is not related to administration of Aspirin.
The most serious damage in Reye's syndrome is associated with the liver and the brain where patients develop fatty liver disease accompanied by minimal inflammation and severe encelopathy accompanied by swelling of the brain. It is essential for Reye's syndrome to be diagnosed early on to avoid possible fatal complications such as severe brain injury or death.
Symptoms and Signs of Reye's Syndrome
Reye's syndrome goes through 5 stages. In the first stage there is generalized lethargy and patients complain about headache. They also vomit profusely, are confused and have increased body temperature. In the second stage minor inflammation of the brain causes stupor, patient's reflexes are hyperactive and there are specific liver changes which may be confirmed by biopsy. In the third stage of the syndrome the symptoms of the first two stages actually progress. Namely, a patient may end up in a coma due to cerebral edema, and in rare cases one may develop respiratory arrest. Stage four features with deepening of the coma, the pupils are large and they do not respond to light. The function of the liver in this stage is minimally affected. And finally, the terminal stage, stage five, features with deep coma, seizures, multiple organ failure and flaccidity. In the terminal stage of the disease the level of ammonia in the blood is above 300mg/dL. The stage five is actually introduction to lethal outcome.
Treatment for Reye's syndrome
Unfortunately, there is no cure for Reye's syndrome. The outcome of the condition basically depends on the stage of the disease and the goal of the treatment is to reduce the brain swelling, reverse metabolic imbalance and prevent all the possible complications. Apart from controlling and maintaining proper function of the brain and the liver it is also essential to prevent complications such as respiratory or cardiac arrest. The treatment is basically symptomatic and the results are better if medications are administered as soon as possible.
Prognosis depends on the severity of the brain swelling. Some patients recover completely. On the other hand, others face varying degree of brain damage. The prognosis is generally poorer for patients who developed coma.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...