Genital herpes is a viral, sexually transmitted disease that affects one in five Americans, with as much as one million of new cases reported each year. This disease is caused by herpes simplex virus type 1. Once a person becomes infected, the virus stays in the body forever, reactivating itself occasionally and causing the symptoms of genital herpes. However, there are people who carry the virus but never actually get the symptoms. Those people can still pass the virus to others.
What is genital herpes?
The main route of transmission of herpes simplex virus is sexual intercourse. An infected person can transmit the virus through vaginal, anal or oral sex. A person who has oral herpes or fever blister can also pass the virus to another person through kissing or through oral sex, causing either oral or genital herpes.
Symptoms of genital herpes
As it is mentioned above, genital herpes can be asymptomatic. This means that a person is infected and does carry the virus, he or she can even pass it on to others, but the actual symptoms are not there. This is relatively common and it occurs in 10 to 20 percent of all people who have the virus.
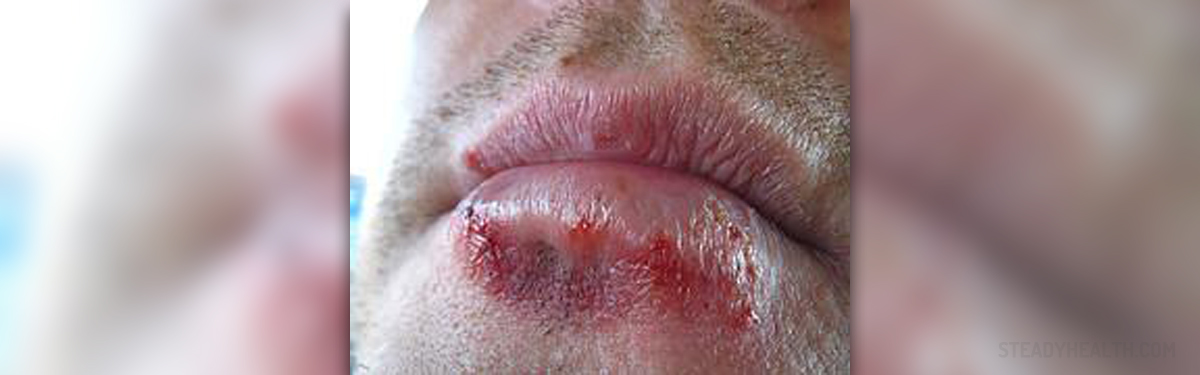
After the virus is passed, it may take two to ten days for the symptoms to appear. At first, the virus cases small red bumps. They eventually turn into blisters and after some time they burst. The bumps, and later the blisters, can appear anywhere in the genital or rectal region- on the vulva, inside the vagina, on the cervix, in the urinary tract, on the penis or on and around the anus. They can also spread to thighs and buttocks.
Aside from these blisters, the symptoms may also include fever, headache, fatigue, muscle ache, swollen glands in the groin, pain and burning when urinating and discharge from the vagina or the penis.
These symptoms are typical for the initial outbreak. As the virus remains in the body, it can reactivate itself and cause recurring outbreaks. This is not a rule and it does not happen to everyone who has the virus. Later outbreaks are usually much milder and rarely involve fever and other flu-like symptoms.
Treatment for genital herpes
The actual virus that causes genital herpes cannot be killed or removed from the body. Certain treatment options are available for reducing the time required for healing during an outbreak and for relieving the symptoms. It is important to keep the area clean and dry and to avoid touching, scratching or irritating the lesions. Oral antiviral medication is recommended because it may shorten the duration of an outbreak. Many doctors prescribe topical antiviral medication as well. Some of the commonly used antiviral drugs for genital herpes are acyclovir, famciclovir and Valacyclovir.
During an outbreak of genital herpes it is highly recommended to avoid sex, even with a condom. After the herpes is cleared, it is still advised to use a condom, because there is still a chance of passing the virus to the partner.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...