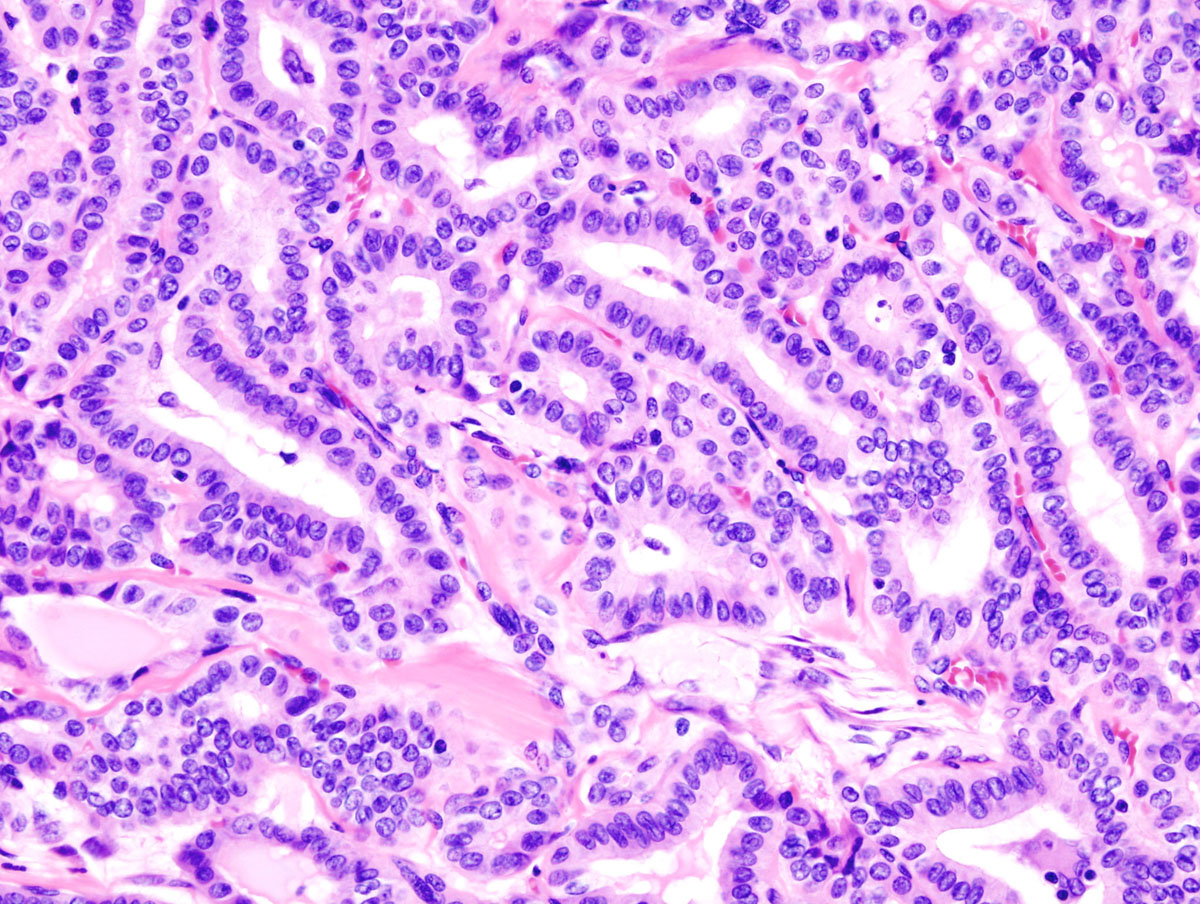
Goiter
Goiter is a medical condition that affects thyroid gland and it features with enlargement of this gland. The thyroid gland in situated in the neck and in normal circumstances it is neither visible nor it can be palpated. Once, the goiter occurs the thyroid gland enlarges. The enlargement can be minimal and only found by physical examination of the patient. On the other side, the thyroid gland can significantly increase so that its enlargement can be easily noticed.
Symptoms of Goiter
Typical symptom of goiter includes swelling at the base of the neck. If the thyroid gland is significantly enlarged patients complain about difficulties with swallowing and breathing. Hoarseness and coughing are additional symptoms of goiter. Imbalance of thyroid hormones typically leads to psychological problems, lack of concentration, increased irritability and sometimes depression.
Causes of Goiter
The leading cause of goiter is lack of iodine in the body. Iodine is crucial substance necessary for production of thyroid hormones. It is taken with certain foods. In case of imbalance in iodine levels and its insufficiency the body cannot produce proper amount of thyroid hormones. The body sends massage to the pituitary gland and it produces thyroid-stimulating hormone which further stimulates the thyroid gland to produce more hormones. But, since there are not enough ingredients for production of thyroid hormones the thyroid gland enlarges and becomes hypertrophic.
Another cause of goiter is chronic thyreoiditis also known as Hashimoto's disease. One of the characteristics of this disease may be enlargement of the thyroid gland. This disease belongs to a group of autoimmune disorders. Apart from Hashimoto's disease another autoimmune disorder called Grave's disease may be a cause of goiter.
Furthermore, goiter may occur in case of thyroid cancer, thyroiditis, genetic defects, and injuries and during pregnancy. The underlying cause of goiter in pregnancy is increased production of human chorionic gonadotrophin, a hormone that may cause enlargement of the thyroid gland.
Diagnosis and Treatment for Goiter
Apart from physical examination the doctor will check thyroid hormones as well as concentration of thyroid-stimulating hormone. This is performed to see whether the patient is suffering from hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism or perhaps the levels of thyroid hormones are normal. Further examination includes ultrasound of the thyroid gland which is an excellent method for identification of newly formed masses, lumps or cysts of the thyroid gland.
The treatment for goiter basically depends on the underlying cause. Hypothyroidism is treated with hormone substitution. There are several treatment modalities for hyperthyroidism and the doctor will choose the most suitable one. Hyperthyroidism can be treated either conservatively or surgically.



-In-Infants-And-Older-Children_f_280x120.jpg)


-During-Pregnancy_f_280x120.jpg)

-And-Children-16-Warning-Signs-And-Symptoms_f_280x120.jpg)
Your thoughts on this
Loading...