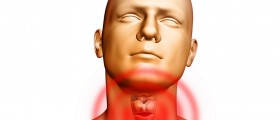
Thyroid gland is a butterfly shaped organ, located in the lower part of the neck. It is an endocrine gland that makes and stores thyroid hormones responsible for regulation of the heart rate, blood pressure and production of energy. In children, thyroid gland is important for growth and development. Thyroid problems are not rare in children and about 5% of the cases are seen in children under age of 15. They may be congenital, inherited or due to iodine deficiency.
Thyroid Problems
There are two types of thyroid problems that develop if any malfunctioning of thyroid gland occurs. They are hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. Hyperthyroidism represents over active thyroid gland while hypothyroidism is under active thyroid gland. Over active thyroid secrets excess thyroid hormones and under active does the opposite, produces thyroid hormones in amount less than required. Both conditions may affect children but each will cause different symptoms.
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism can be caused by different conditions. Neonatal hyperthyroidism is over active thyroid gland present at birth. This condition is rare but may occur if the mother suffers from the Grave’s disease. Symptoms of neonatal hyperthyroidism are increased heart rate, irritability, increased appetite and poor weight gain. Hyperthyroidism in children is most commonly due to Grave’s disease. It occurs when antibodies produced by the body stimulate thyroid gland which than secretes excess thyroid hormones. Symptoms of Grave’s disease include hyperactivity, restlessness, trouble concentrating at school, weight loss, trouble sleeping, diarrhea, behavioral problems and fast heartbeat.
Hypothyroidism
Under active thyroid gland is associated with few conditions. They include congenital hypothyroidism and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Congenital hypothyroidism occurs when thyroid gland doesn’t fully develop in newborns. In rare cases thyroid gland may be absent, abnormally located or severely reduced in size. Symptoms of the condition include poor feeding, jaundice, sleepiness, constipation and low body temperature. Congenital hypothyroidism can be treated with hormone replacement therapy. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune disorder and may occur at any age. Early symptoms include delay in skeletal development, thyroid gland inflammation, sensitivity to cold, weight gain, trouble concentrating and low energy levels. The treatment involves life long hormone replacement therapy.
Symptoms of Thyroid Problems in ChildrenSymptoms of thyroid problems in children vary depending on the type of thyroid disorder. Hyperthyroidism in children causes extreme hunger, shakiness, more frequent bowel movements, irritability, poor concentration, mood swings, insomnia, restlessness, hyperactivity, loss of hair, unusual sweating and enlargement of thyroid gland. Symptoms of hypothyroidism are goiter, weight gain, poor appetite, dry skin, cold intolerance, delayed growth, constipation, hoarse voice, fatigue, depression, pale skin and swollen tongue.
Treatment for Thyroid Problems in ChildrenThe treatment is determined according to the cause of thyroid problem. Hyperthyroidism is initially treated with medications that help in regulation of thyroid hormones production. However, if there is no improvement after 2 years of treatment with the medications, surgical removal of the thyroid gland may be required. Hypothyroidism generally responds well to treatment and the condition can be cured in most of the children.




-In-Infants-And-Older-Children_f_280x120.jpg)
-And-Children-16-Warning-Signs-And-Symptoms_f_280x120.jpg)



-During-Pregnancy_f_280x120.jpg)
Your thoughts on this
Loading...