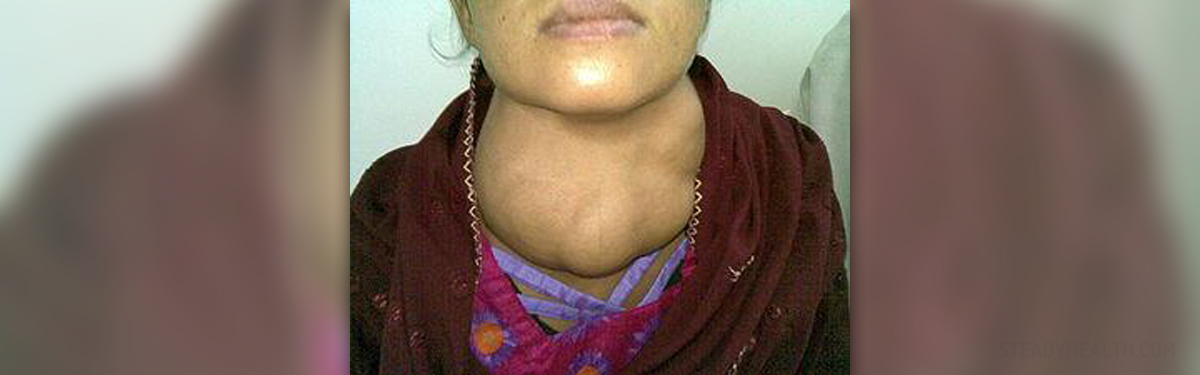
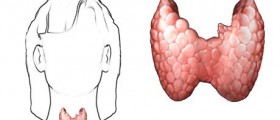
Goiter is a condition characterized by an enlargement of the thyroid gland which causes the neck to appear swollen. Goiter is associated with abnormal functioning of the thyroid gland.
Goitre Overview
The thyroid gland is a small endocrine organ, located in the neck below the Adam’s apple. This gland secretes hormones that regulate body’s metabolism. Normally, the thyroid gland is not visible from the outside, but enlargement of the gland causes lump to form in the throat, or a goiter.
This mass can be of different size. A small goiter generally does not cause any symptoms. However, a large goiter can put pressure on the windpipe and esophagus leading to difficulty breathing and swallowing.
Goitres can occur due to different reasons. This includes an overactive thyroid gland, the condition known as hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, which is the medical term for an underactive thyroid gland. Pregnancy can also give rise to development of goiter. Iodine deficiency is the most common cause of goiter worldwide.
Treatment for Goitre
Treatment for goiter is determined by the underlying cause. Watchful waiting is the usual treatment approach when goiter is small and does not produce bothering symptoms.
If the goiter is big or the symptoms are present, treatment options include dietary supplements, thyroid hormone replacement therapy, radioactive iodine and surgery.
A goiter caused by hypothyroidism is commonly treated with synthetic thyroid hormone called levothyroxine. This hormone is taken by mouth usually once a day. The patient may experience side effects of this treatment such as chest pain, irregular or rapid heart beat, muscle cramps and weakness, vomiting, diarrhea, tremor, headaches, increased sweating and weight loss. These side effects subside once the body gets used to the medication.
A goiter caused by overactive thyroid gland can be managed with thionamides or radioactive iodine. Thionamides are also taken orally. This medication acts by decreasing production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. Side effects of thionamides include joint pain, skin rash, nausea and itchy skin. In very rare cases, agranulocytosis may occur. It is a serious condition marked by a sudden drop in the number of white blood cells.
Radioactive iodine is another treatment option for overactive thyroid. It works by destroying the thyroid cells and reducing the size of the goiter. Iodine supplements are standard treatment for goiter caused by iodine deficiency.
Surgical removal of the thyroid gland is typically used when the condition does not respond to other treatment options and symptoms are severe. In this procedure part or the entire gland can be removed. Lifelong hormone replacement therapy may be necessary in addition to this treatment.Prevention of Goitre
There are no ways to prevent goiter unless it is caused by iodine deficiency. Dietary measures to prevent iodine deficiency include use of iodized table salt and consumption of rich sources of iodine such as seafood.


-In-Infants-And-Older-Children_f_280x120.jpg)



-During-Pregnancy_f_280x120.jpg)
-What-Are-Your-Options_f_280x120.jpg)
-And-Children-16-Warning-Signs-And-Symptoms_f_280x120.jpg)
Your thoughts on this
Loading...