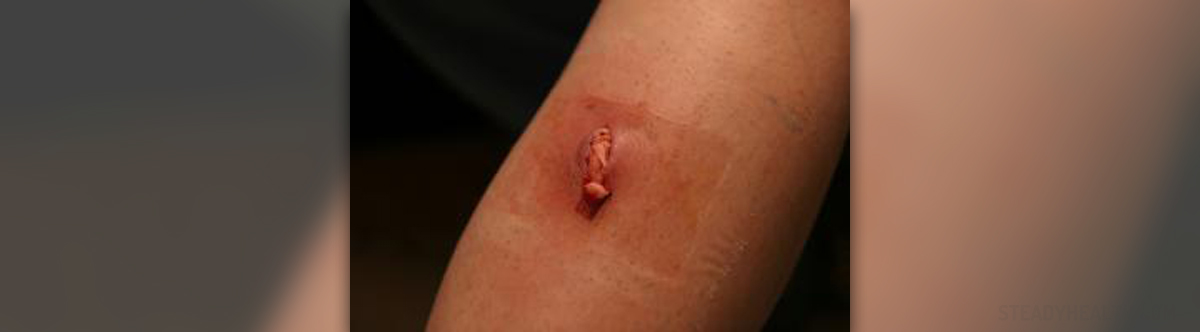
A staph infection is an infection caused by bacteria of Staphylococcus genus. These bacteria are normally present in many people, in fact about one quarter of all people carry them in their nose, mouth, genitals and anal area. Staphylococcus is also fairly easy to pick up from the ground with feet.
The infection usually starts after the bacteria penetrate a small cut or opening in the skin.
The severity of staph infections can range from simple boils, to infections with strains that are resistant to antibiotics, and in most severe cases to flesh-eating infections.
What makes the difference between different degrees of infection is how far or deep it has spread, if it is treatable with antibiotics, how fast it spreads and how soon it was diagnosed.
The fact that in some cases the infection cannot be treated with antibiotics, because the bacteria are resistant, should warn people against the antibiotics overuse, which is, unfortunately, quite common in North America.
A staph infection can also cause cellulitis, a disease which affects deeper layers of the skin, and which is treatable with antibiotics.
People who are particularly prone to this common disease are those whose immune system is weakened, as well as persons who suffer from diabetes.
Symptoms of staph infection
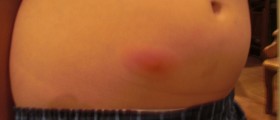
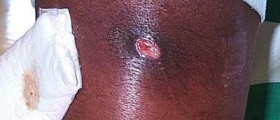
If a staph infection affects the skin, the symptoms usually include localized redness, swelling, and collection of pus in form of abscess or boil.
The infection may or may not start with an open sore on the skin.
If the bacteria penetrate the skin, they cause sepsis or bacteremia, characterized by fever, chills and low blood pressure.
Treatment for staph infection
Staph infections are treated with antibiotics, which kill bacteria. After the staphylococcus bacteria were first discovered, they were usually treated with penicillin. However, today doctors prefer stronger antibiotics and penicillin is no longer the first choice when it comes to treating a staph infection.
The problem is that in 50 percent of cases the bacteria may be resistant even to the strong antibiotics. This is why doctors are, or should be, more cautious when it comes to prescribing antibiotics. Overuse of antibiotics may lead to resistance and in those cases the treatment of staph infections is very difficult.
In case the infection has spread so deep that it affected multiple tissues, like muscles and fibers that surround them, there may be a need of a surgical intervention to clean the area.
Staph infections can be prevented by cleaning all cuts, scrapes and other wounds with antibacterial soap and similar sterilizing products. An infection can spread to others especially if it is in a phase when one or more boils weep and drain.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...