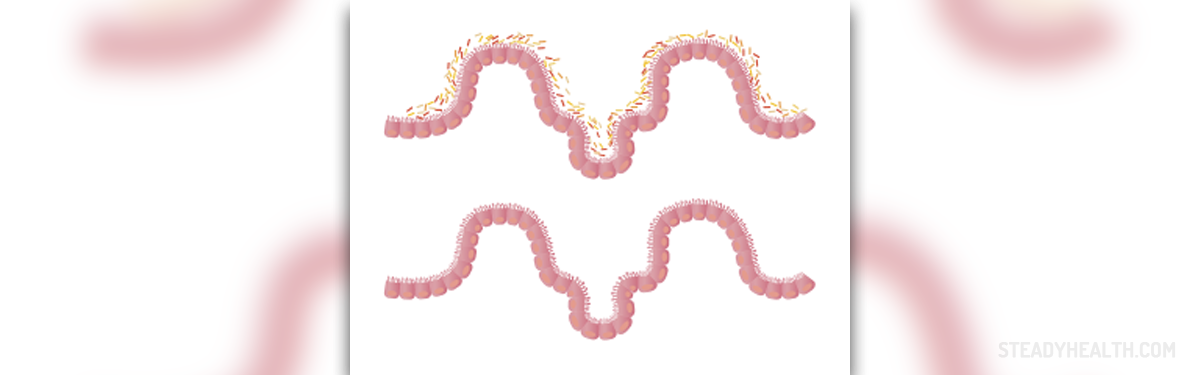
Causes of viral intestinal infections
Several different viruses can cause stomach flu. Adenovirus causes infection mostly in young children, ages two and below. This virus strain affects the inner lining of the intestines and cause diarrhea and vomiting. In most cases the symptoms start approximately one week after infection. Some children are particularly prone to this infection and can suffer from it several times a year.
Astovirus is particularly active during winter, and it mostly affects babies, young children, and elderly. The symptoms tend to start three days upon infection.
Calciviruses are divided in four types, the most common of them being nonovirus. They affect people of all ages and may cause epidemics especially around October. The symptoms also include fatigue and muscle pain.
Rotavirus affects mostly young children aged between three and 15 months. Adults can contract the virus from children but their symptoms are much milder. This virus causes abdominal pain and fever, and it is particularly active from November to April.
Symptoms of viral intestinal infections
Although the symptoms may vary depending on the specific strain of the virus, they generally include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite, dehydration due to loss of fluids through vomiting and diarrhea, fatigue, abdominal pain, low grade fever and headache.
The symptoms may last anywhere from two to ten days, and this too depends on the virus, but also on the severity of the infection.
Treatment for viral intestinal infections
After a person seeks medical attention for symptoms of stomach flu, doctors may diagnose a viral infection based just on the physical exam and symptoms, or they may order a set of tests, usually of stool samples, to determine the presence and the specific type of the virus.
Doctors usually recommend rest until the symptoms subside, and they also insist that the patient takes enough fluids to replenish those lost due to diarrhea and vomiting and thus to prevent dehydration. People who suffer from a viral intestinal infection should avoid fatty, greasy and spicy foods, dairy products, coffee and alcohol. It is best to drink boiled water, thoroughly cooked vegetables, rice, saltines and similar foods.





_f_280x120.jpg)










Your thoughts on this
Loading...