Many parts of our body are covered with or contain certain bacteria that are considered normal inhabitants. This is also the case with the vagina. The vagina contains certain types of bacteria not harmful to the lining of the organ or upper parts of the female reproductive system. These microorganisms are in charge with production of acid, the powerful substance that prevents infections caused by other bacteria as well as fungi or viruses. In case the level of acidity is affected and reduces, the chances or vaginal infections increase significantly.
What are Vaginal Infections?
Vaginal infections are those affecting the vagina They are always caused by some harmful microorganisms that settles in the vagina (on its surface), start to multiply and trigger local inflammatory response. The presence of the infectious agents is to blame for inflammation of the vaginal lining and formation of abnormal discharge of different characteristics.
Vaginal discharge that accompanies vaginal infections is of unusual color and unpleasant odor. There are also symptoms and signs of vaginal and vulvar irritation such as itchy or burning sensation, pain during sexual intercourse or abdominal pain. A woman may also notice redness of the vulva or sometimes there are lumps, blisters or ulceration covering the area.
All in all, vaginal infections are considered relatively common, mostly affecting women in their reproductive years. Fortunately, almost all of these are curable and treated with success.
Types of Vaginal Infections
There are several types of vaginal infections. They are easily classified according to infectious agents responsible for the very infection. So, there are bacterial, fungal and viral vaginal infections. Parasitic bacterial infections may occur as well.
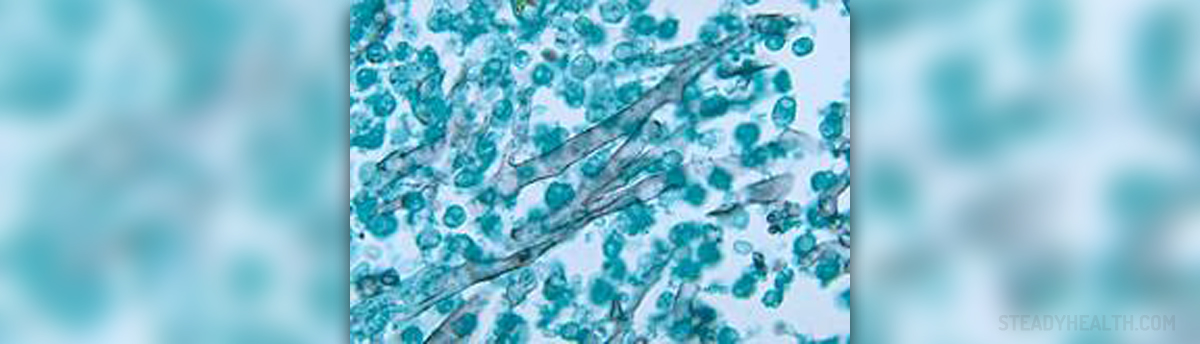
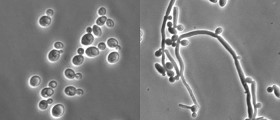
One of the most commonly reported vaginal infections is thrush. It develops as a result of excessive multiplication of Candida albicans due to a change in the vaginal environment. Thrush occurs as a consequence of many potential triggers some of which are pregnancy, excessive use of antibiotics and is also associated with certain underlying conditions that make the immune system weak.
Bacterial vaginosis is also frequently reported and affects many women all around the world. Discharge in this case becomes yellow or grayish and is of rather unpleasant odor ('fishy' smell). Bacterial vaginosis is many times connected with the use of perfumed soaps, feminine hygiene sprays and intra-uterine system. Some bacteria are transmitted via sexual contact with infected person. It is essential to treat such infections correctly and avoid potential complications.
Chlamydia is a frequent bacterial infection and one of the most common sexual transmitted disease around the world. Apart from potentially affecting the vagina, Chlamydia is blamed for destruction of cervical cells and other reproductive tissues. The bacterium may spread to the uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes and trigger pelvic inflammatory disease, an underlying cause of ectopic pregnancies and infertility. Gonorrhea is one more type of bacterial vaginosis. This sexually transmitted disease is accompanied by abundant vagina discharge, painful urination, bleeding between period and pelvic/abdominal pain of varying degree.
Viruses are additionally blamed for vaginal infections. Genital herpes and genital warts are the most common viral infections affecting this area. They are caused by different viruses and have different course of the disease. In genital herpes the vulva and vagina are covered with painful blisters that burst easily. Soreness is very intense and there are sometimes additional problems with passing urine. Genital herpes is a recurrent condition, mostly triggered by stress, friction or immunodeficiency. Genital warts are cauliflower growth that form in the vulvar area, inside the vagina or may also affect the upper thighs, cervix or anus. The infection requires surgical approach in many cases while the virus cannot be completely eradicated from one's body.
And finally, there are not that many parasites causing inflammation of the vagina. Trichomonas vaginalis is one of them. The infection is transmitted via unprotected sex and is a cause of a heavy, frothy, yellow-green discharge. The smell of discharge is obnoxious, resembling a fishy smell. It is also possible to suffer from trichomoniasis and have no symptoms at all.
Vaginal Bacterial Infections - Treatment and Prevention
Bacterial vaginosis is relatively easily treated since there are plenty of efficient antibiotics doctor can opt for. It is, however, important to determine the exact bacterium responsible for the infection and check whether it is sensitive to antibiotic that is going to be prescribed (best achieved with the assistance of antibiogram). Some bacteria are efficiently eradicated by metronidazole gel or clindamycin cream (both applied directly into the vagina) while more complex cases are treated with metronidazole tablets (oral route of administration).
As far as prevention is concerned, it is best achieved if women use condom each time they have sexual intercourse, limit the number of sexual partners, abstain from douching and apply some less radical measures. These include wiping from the front to the back after using the toilet, wearing loose fitting jeans and underwear made of natural fiber such as cotton. It is also good to avoid perfumed feminine hygiene products and have regular baths.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...