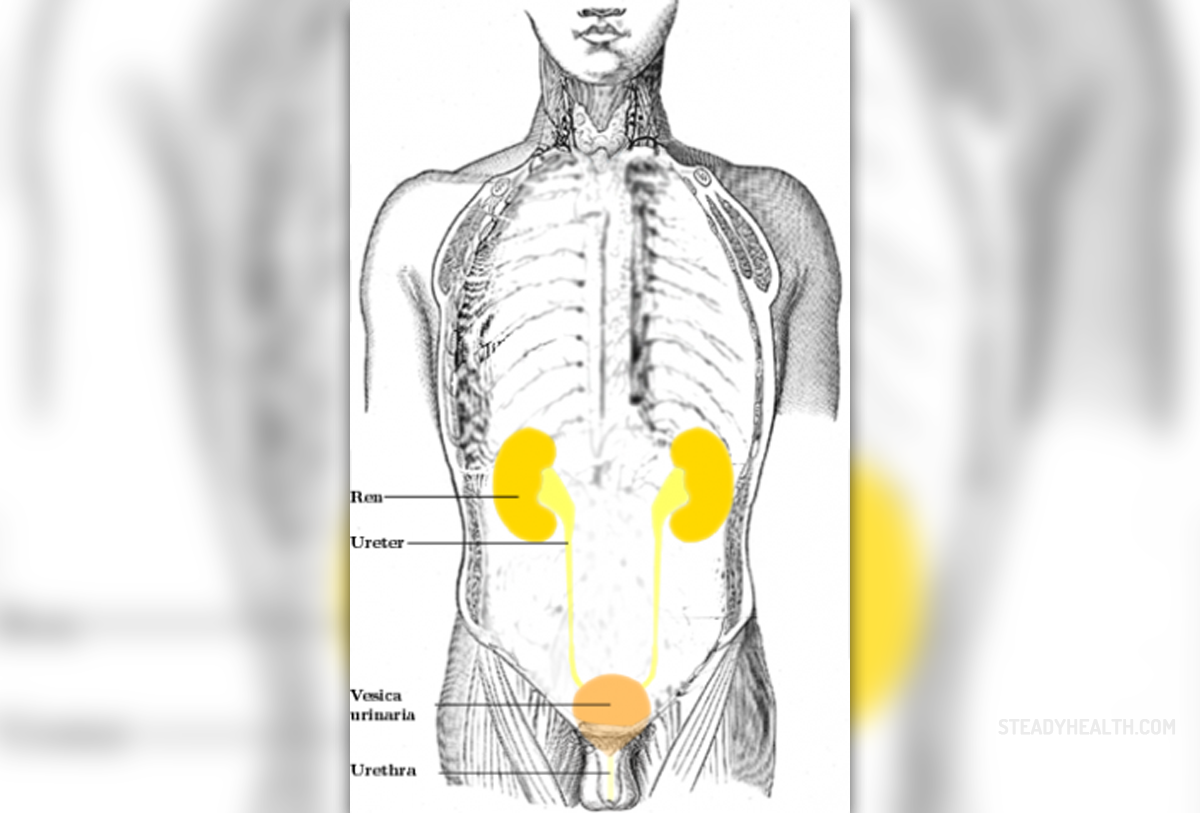
The urinary system is a set of body parts that play a specific role in the body. The main principle of the urinary tract is to filter out the excess fluid and other substances from the bloodstream. Basically, urinary system maintains the amount and composition of body fluids within normal limits, and regulates the concentrations of various electrolytes in the body fluids and maintaining normal pH of the blood. The human urinary system includes two kidneys, two ureters, the bladder, the urethra and two sphincter muscles. The excess fluids and substances (such as excess minerals and vitamins) are filtered out from the body in the form of urine which is produced by the kidneys, collected in the bladder and excreted through the urethra.
Kidneys
Kidneys are bean-shaped organs placed around or just below the ribcage and close to the lumbar spine. The main role of kidneys is to filter water soluble waste products from the blood. Normally, kidneys receive the blood supply of 1.25 L/min from the renal arteries. Humans normally have two kidneys and at least one of them must function properly for life to be maintained. Kidneys have six major functions: regulation of plasma ionic composition, regulation of plasma osmolarity, regulation of plasma volume, regulation of plasma hydrogen ion concentration (pH), removal of metabolic waste products and foreign substances from the plasma and secretion of hormones. Kidneys produce hormone known as renin, which stimulates the secretion of aldosterone. The kidneys also secrete erythropoietin, which stimulates the red blood cell production.
Ureters
In human anatomy, ureters are small tubes that proper urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. Each tube is about 10 inches or 25 cm long. In females, the ureters pass through the mesometrium and under the uterine arteries on the way to the urinary bladder. After the urine enters the bladder from the ureters, small folds in the bladder mucosa act like valves preventing backward flow of the urine.
Urinary Bladder
The urinary bladder is the organ that collects urine excreted by the kidneys before disposal by urination. This is a hollow muscular and elastic organ situated on the pelvic floor. The urinary bladder can hold approximately 17 to 18 ounces (500 to 530 ml) of urine. People normally feel the need to urinate when the bladder accumulates somewhere around 150 to 200 ml of urine. The urine bladder plays a significant role in the regulation of body temperature. When the bladder becomes empty patients usually experience the chilling sensation and get a relief from high temperature.
Urethra
Urethra is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the genitals for the removal of urine out of the body. In males, the urethra travels through the penis while in females urethra is shorter and emerges above the vaginal opening. Because the urethra is so much shorter in women, they are more prone of developing bacterial and urinary tract infections.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...