Down syndrome, also known as trisomy 21 is a chromosomal condition that is caused by presence of all or part of an extra 21st chromosome. This condition is relatively rare and one case happens per every 733 births. In most cases, Down syndrome is seen in the offspring of older parents, including both mothers and fathers. There are many other risk factors involved in development of this disease, but parental age remains one of the most prominent, as older parent’s reproductive cells usually go through increased mutagenic exposures. Something similar to Down syndrome is also been discovered in other animal species, including chimpanzees and mice.
Chromosome abnormality and Down syndrome
Chromosomal condition or chromosome abnormality is any kind of atypical number of chromosomes or a structural abnormality in one or more chromosomes. A chromosome is an organized structure of DNA proteins in cells. In most cases, chromosome abnormalities occur because of an error in cell division, and they are typically classified as numerical or structural disorders.
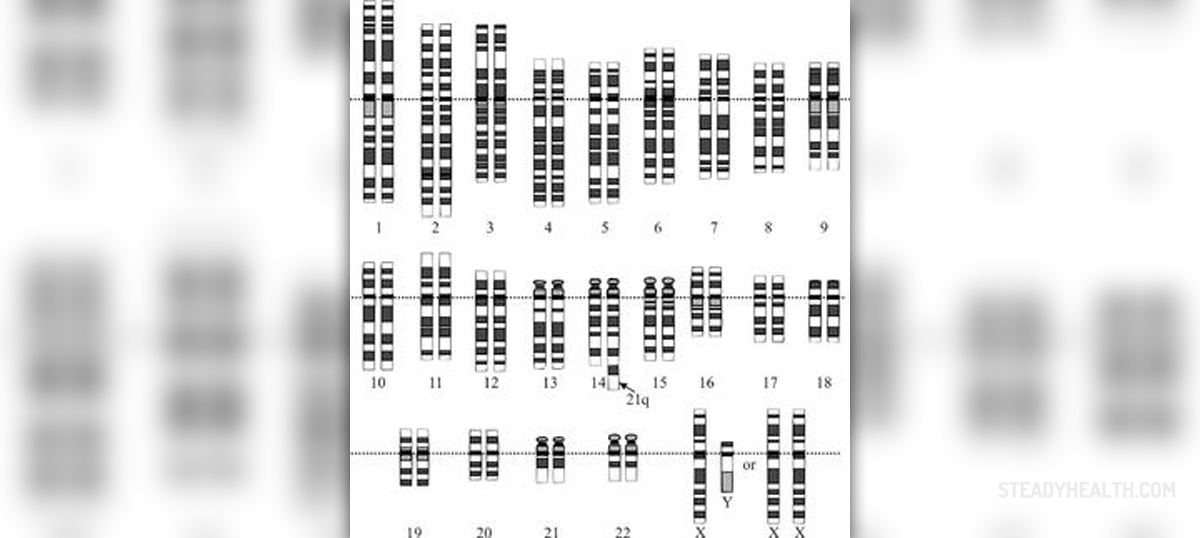
In the case of Down syndrome, chromosome abnormality belongs to a type of numerical disorders. Numerical disorders occur when a person is either missing a chromosome from a pair (monosomy), or having more than two chromosomes of a pair (trisomy, tetrasomy, etc.). A person suffering from Down syndrome actually has three copies of chromosome 21, instead of normal two copies. This is why the condition is often called trisomy 21.
Chromosome 21 is only one of 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. It is the smallest human chromosome that most probably contains between 300 and 400 genes. Any kind of change in the number or a structure of this chromosome can lead to many various effects including developmental delay, mental retardation and characteristic facial features.
Down syndrome genetics
Most people affected with Down syndrome have an extra copy of chromosome 21. In these cases, the condition is a result of trisomy 21, where a body has three copies of chromosome, which disrupts normal course of development and causes other characteristic signs and symptoms.
Small number of people suffering from Down syndrome actually has an extra copy of chromosome 21 only in some of the body cells. This condition is known as mosaic Down syndrome and it is characterized by a bit milder intellectual impairment. However, this subtype accounts for only about 2 to 4% of all cases of Down syndrome.
Down syndrome can also happen when a part of chromosome 21 becomes translocated to another chromosome. This usually happens during the formation of reproductive cells or in early days of fetal development. This sub-type is known as translocation Down syndrome and it accounts for 4 to 5% of Down syndrome cases.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...