Trisomy 13 syndrome also known as Patau syndrome is a genetic disorder featured by three copies of chromosome 13. The lifespan of infants born with trisomy 13 syndrome is only a few days.
Trisomy 13 Syndrome Overview
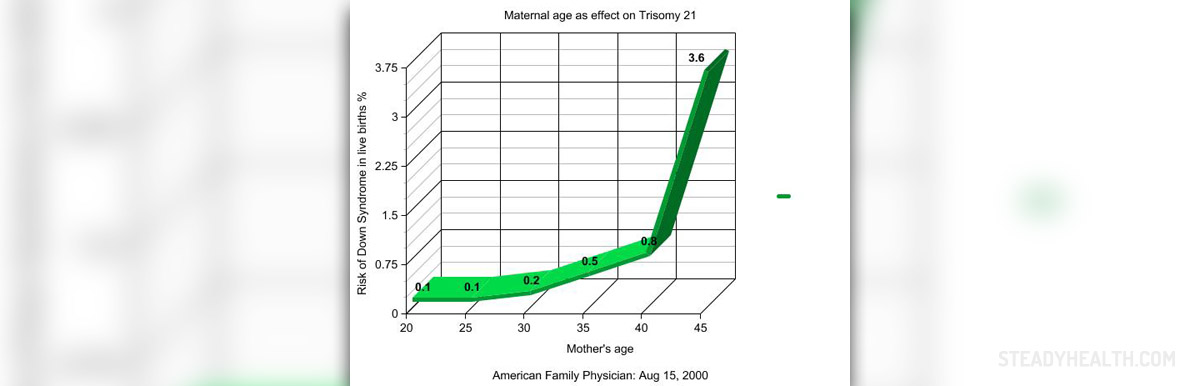
Trisomy 13 syndrome is very rare chromosomal abnormality. Among autosomal trisomies, trisomy 13 syndrome is the least common and the most severe disorder. In most cases survival rate for children with the syndrome is 2.5 days. Originally, trisomy 13 syndrome was identified as cytogenetic syndrome.
Causes of Trisomy 13 Syndrome
Trisomy 13 syndrome is caused by extra chromosome 13, which is a medium-length acrocentric chromosome. Children normally inherit two copies of chromosome 13 from each parent. However, in individuals affected by the syndrome, every cell in the body has three copies of the chromosome. This additional chromosome 13 causes multiple birth defects.
In some cases, children may be born with milder form of trisomy 13 syndrome in which only some cells have the extra chromosome 13. This is known as Mosaic Patau syndrome.
Trisomy 13 syndrome may also be caused by translocation of the chromosome. In such case, affected person does not have three copies of chromosome 13 but two copies and extra material from chromosome 13 attached to another chromosome. This results in partial trisomy of chromosome 13.
Most cases of trisomy 13 syndrome are not inherited but occur randomly during cell division in early development of a fetus or during formation of reproductive cells such as eggs and sperm. However, the syndrome caused by translocation of chromosome 13 is associated with inheritance.
Symptoms of Trisomy 13 Syndrome
The syndrome typically manifests in profound mental retardation. Trisomy 13 syndrome is commonly accompanied with holoprosencephaly, a birth defect of the brain that also affects facial features. Cleft lip, cleft palate, nasal malformation and abnormally closed eyes are commonly seen in infants with trisomy 13 syndrome.
The syndrome is also associated with cardiac defects such as ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect and others. Urogenital malformations like polycystic kidneys and abnormal genitalia are commonly present too. Trisomy 13 syndrome causes gastrointestinal abnormalities as well. Abnormalities of the hands and feet are also common. This includes extra toes and fingers (polydactyly), rocker-bottom feet and palm deformities. Affected children are usually deaf and have low-set ears.
Diagnosis and TreatmentTrisomy 13 syndrome can be diagnosed with the help of chromosome analysis. MRI and CT scan help to identify holoprosencephaly, in which the brain does not divide into two halves. The syndrome cannot be cured and treatment is very difficult due to numerous defects. The treatment is commonly supportive and rarely aims to prolong life.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...