
Down syndrome, a chromosomal condition also known as trisomy 21, is a severe developmental condition caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21. Down syndrome affects children as soon as they are born. John Langdon Down, an English physician, first diagnosed this condition and an essay about it was first published in 1866. However, it was not before 1959 when a scientist Dr. Jeremy Lejeune discovered the true cause of this condition - an extra 21st chromosome. According to the official statistics, about one per each 800 babies is born with Down syndrome. In most cases, these children are born to older parents.
Causes of Down syndrome
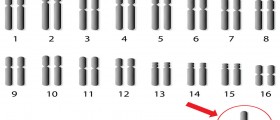
Down syndrome, as a chromosomal condition, occurs when a certain error happens during the cell division. These errors can be numerical or structural, and changes on the chromosome 21 are a special type of numerical disorder in which an individual has more than two chromosomes of a pair. Normally, people have 46 chromosomes per cell, and each cell contains 23 pairs of large linear nuclear chromosomes. When the error in cell division occurs, human cells sometimes get an additional chromosome 21, instead of normal two. This condition is known as trisomy (having three chromosomes).
Signs and symptoms of Down syndrome
This extra genetic material on chromosome 21 causes various developmental problems in affected individuals. This condition is associated with typical physical characteristics, mental problems and health-related problems. The exact signs and symptoms may vary from one patient to another due to complex gene and environment interactions. Most of the affected individuals share some common features. For example, all of the patients are mentally retarded, to some extent, their growth is also stunned, their fingertips usually have an atypical shape, and they may have asingle transverse palmar crease. Moreover, muscle tone of these patients is usually very poor; they mostly have a short neck, white spots on the iris and a flat nasal bridge. Medical problems associated with this condition are congenital heart defects, respiratory problems, gastrointestinal disorders, and increased susceptibility to infection.
Risk factors
One of the most severe risk factors of having a baby with Down syndrome is a maternal age. By the age of 35, woman’s risk of having a child with Down syndrome is 1 in 400. Only ten years later, this risk rises to 1 in 35. However, most of the babies with Down syndrome are born to women under age 35. This happens because younger women have far more children.
Males can also pass the genetic translocation for Down syndrome on to their children, if they are carriers.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...