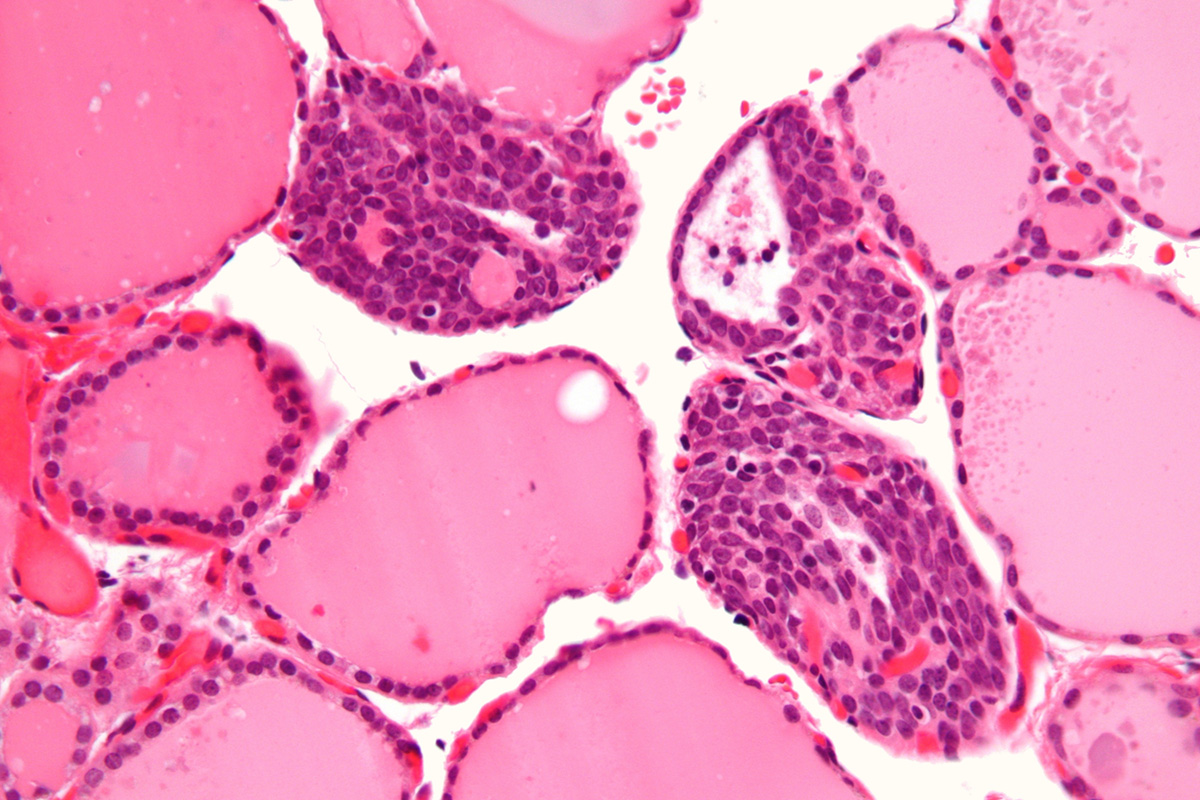
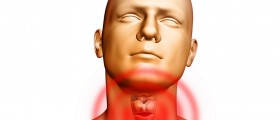
Thyroid storm is life-threatening condition that occurs due to untreated hyperthyroidism (over active thyroid gland).
Causes of Thyroid Storm
Hyperthyroidism develops when a thyroid gland, which is located at the front part of the neck, starts to release too much of thyroid hormones. Hyperthyroidism can cause fatigue, goiter (enlarged thyroid), heat intolerance, sweating, increased appetite, rapid heartbeat or palpitations, weight loss and protruding eyes. If hypothyroidism is not adequately treated, thyroid hormone levels may significantly increase leading to worsening of the symptoms and condition known as thyroid storm. Thyroid storm can also be caused due to illness or severe infection, particularly of the lungs. Taking large amounts of the thyroid hormone, getting too much iodine, discontinuing medications for hyperthyroidism, heart attack, thyroid surgery and pregnancy can also lead to thyroid storm in patients with hyperthyroidism.
Symptoms of Thyroid StormSymptoms of thyroid storm are more severe than those of hyperthyroidism. They include elevated body temperature (105-106º F), rapid heart rate and shortness of breath. A person usually also experiences chest pain, increased sweating, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anxiety and irritability, weakness and heart failure. Immediate medical attention is required in case of very rapid heart beat, fever, extreme fatigue and tiredness and confusion and disorientation.
Diagnosis of Thyroid StormTo diagnose thyroid storm a doctor will order a blood test to evaluate thyroid function. Blood cell count, levels of electrolyte, blood sugar level and levels of thyroid hormone will be measured. Liver function test is usually required too.
Treatment for Thyroid StormThyroid storm is accompanied with severe symptoms and although rarely occurs it is an emergency and may lead to death. Thereby, this condition requires hospitalization and emergent treatment. Firstly, the cause of thyroid storm must be identified. A patient has to receive intravenous fluids and electrolytes. Oxygen may be given if necessary. Fever can be reduced with medications such as antipyretics but cooling blankets may be used as well. Intravenous corticosteroids such as Hydrocortisone can be given to support the blood circulation. Thyroid hormone synthesis can be reduced with medications that block the production of thyroid hormones and they include propylthiouracil (PTU) and methimazole. Thyroid hormone release can be inhibited with sodium iodine, potassium iodine or Lugol’s solution. Beta-blockers like propranolol (Inderal) are given to control the heart rate and block the action of thyroid hormones on the cells. If a patient has suffered heart failure it has to be treated as well. After recovery from thyroid storm, further treatment may include radioactive iodine or antithyroid medications.









-In-Infants-And-Older-Children_f_280x120.jpg)
Your thoughts on this
Loading...