
Wilson's disease is a disorder characterized by excessive accumulation of copper in the body. This improper regulation of copper absorption and elimination is hereditary and excess of copper accumulates into many organs such as the liver, brain etc. This causes serious damage to the affected organs and they may even eventually, if the condition is left untreated, completely lose their function.
Wilson's Disease - Overview
Even though copper plays significant role in many processes in the body, its excess is always detrimental. This element is absorbed from the food and eliminated via bile.
Due to its presence in large amounts and accumulation in different tissues and organs patients suffering from Wilson's disease usually complain about symptoms and develop signs according to the affected organ. The most frequent symptoms and signs of this disorder include clumsiness, difficulty speaking, swallowing or walking, drooling, depression and involuntary shaking. Furthermore, patients may also bruise easily, complain about fatigue and joint pain, loss of appetite and nausea. Skin rash, swelling of the arms and legs and jaundice are several more characteristics of Wilson's disease.
Accumulation of copper and its inadequate elimination from the body develops as a consequence of a genetic mutation. The disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning that both parents must have a defective copy of the gene called ATP7B.
Therapy for Wilson's Disease
It is essential to diagnose Wilson's disease and start with treatment as soon as possible since excess of copper may cause serious complications such as liver cirrhosis and subsequent liver failure or persistent neurological problems. Such patients are also prone to kidney stones.
Treatment for Wilson's disease includes medications which prevent excessive absorption of copper from the intestine and those which can reduce the amount of copper in the body. Patients with severe liver damage (end stage liver cirrhosis and liver failure) must undergo liver transplant surgery.
Drugs capable of removing excess of copper from the body include chelating agents. They bind copper and allow its elimination via kidneys. These include penicillamine and trientine. It is essential to monitor patients during treatment because these drugs have many serious side effects.
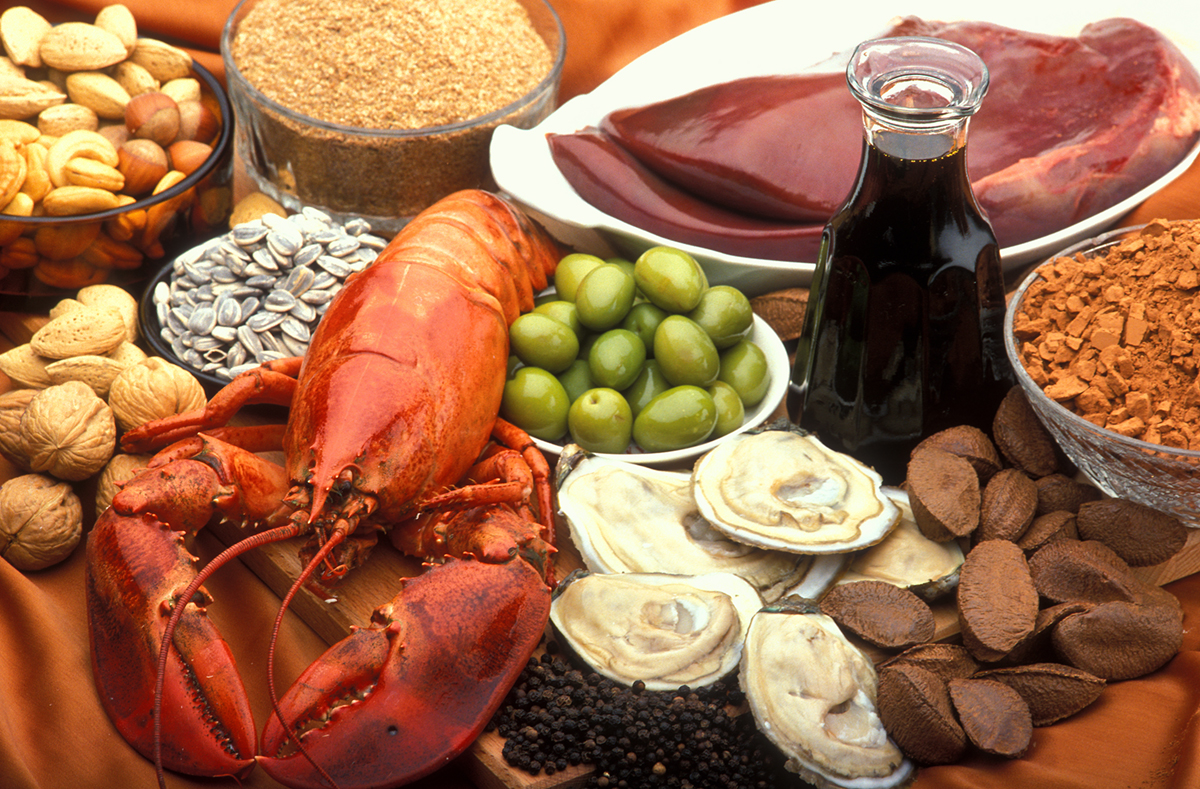
A drug that can prevent excessive absorption of copper from the intestine is zinc acetate. It is also important to pay close attention to food and food products which contain a lot of copper. These should be avoided and limited during the first year of treatment. Plenty of copper is found in liver, fish, shellfish, mushrooms, nuts, chocolate, drier fruit, dried peas, beans and lentils and avocados. And finally, bran products contain a lot of copper too.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...