
Peritoneal Cavity
The peritoneal cavity is one of the three cavities in mammals and represents the largest seroseal sac in the human body. It is located in the abdomen. The other two cavities are pleural and pericardial cavity. The peritoneal cavity is a space bordered with the peritoneum, a membrane which consists of two layers, visceral and parietal peritoneum. Both of these layers are transparent and highly permeable.
The peritoneal cavity is anatomically divided into two separate sacs. The bigger sac consists of two compartments called supracolic and infracolic compartment. They are separated by the transverse colon. The supracolic compartment contains the liver, gallbladder and stomach. Intestines are situated in the infracolic compartment. On the other side, smaller sac of the peritoneum is anatomically known as omental bursa and is located behind the stomach. It communicates with the rest of the peritoneal cavity via the epiploic foramen.
Peritoneal Cavity Organs
Peritoneal cavity contains many important organs. All of them are classified as intraperitoneal organs and extraperitoneal organs. Intraperitoneal organs include the liver together with the gallbladder, the transverse colon and small intestine. The previously mentioned organs are covered with peritoneum and are supported by mesentery. On the other hand, retroperitoneal organs, also known as extraperitoneal organs are only partially covered with peritoneum and they are not supported by the mesentery. These organs include the duodenum, pancreas, both kidneys, the uterus, the bladder, ascending and descending colon.
There is a difference between male and female peritoneum. Namely, in men this cavity is closed while in women peritoneal cavity communicates with the reproductive organs. The communication is possible thanks to the oviducts which open laterally into the peritoneal cavity. This communication makes women more susceptible to peritoneal infections.
The peritoneal cavity is filled with a small amount of fluid. The fluid is light yellow in color and its basic purpose is lubrication of the peritoneum and prevention of excessive friction between the peritoneum and organs in the peritoneal cavity. Peritoneal fluid normally contains leukocytes, antibodies and several more substances. In certain illnesses such as liver cirrhosis the amount of peritoneal fluid may drastically increase. Excessive accumulation of the fluid inside the peritoneum is medically known as ascites. The presence of ascites causes distension of the abdomen and is usually followed by extreme fatigue and may in severe cases lead to shortness of breath, particularly if it is also accompanied by accumulation of the fluid in the pleura. People who are suffering from ascites are given diuretics to eliminate excess of fluid.
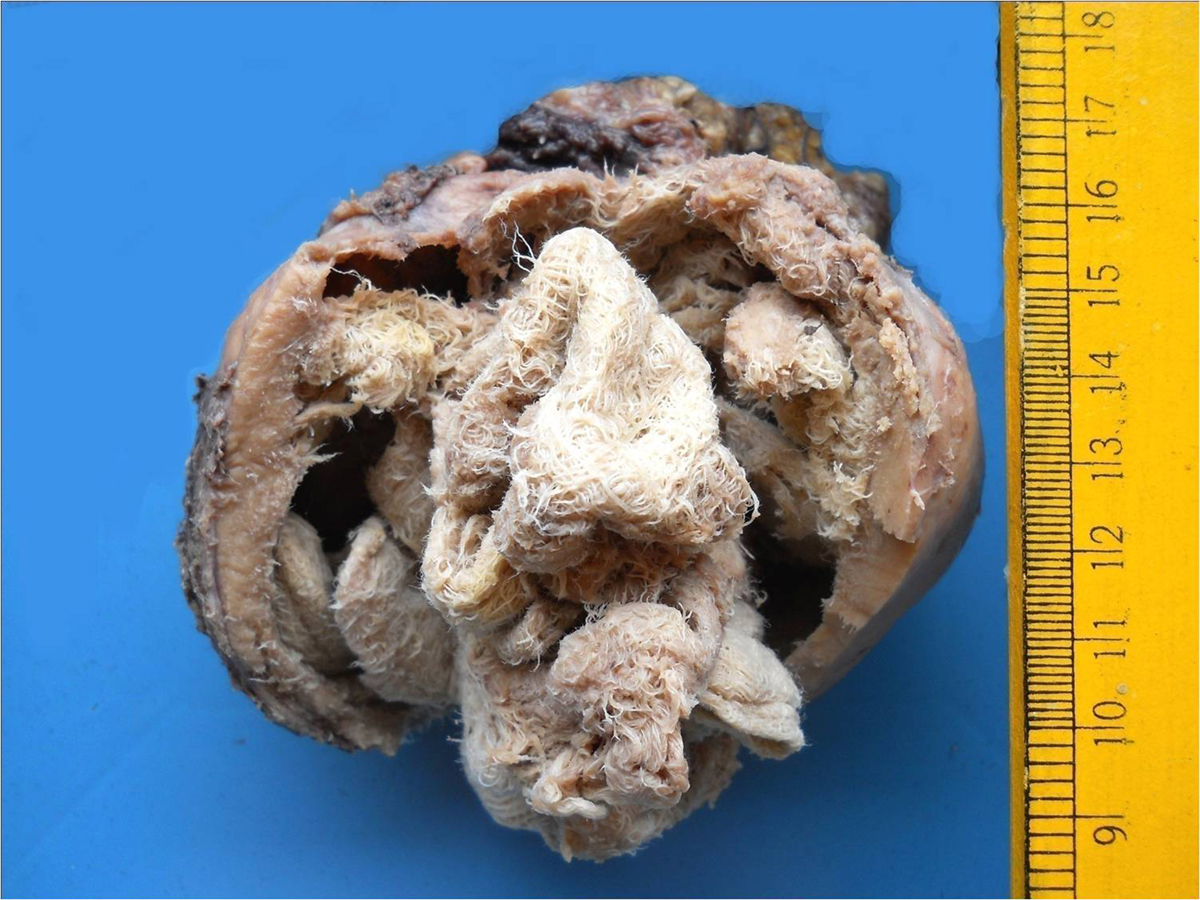
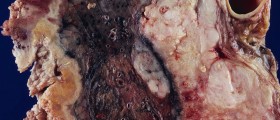
Peritoneal cavity can be affected by the cancer. This type of cancer is known as peritoneal mesothelioma. It occurs rather rarely. The tumor may grow for some time without causing any symptoms. Once the tumor has reach significant size or has spread to the surrounding tissues and organs it may cause nausea, frequent urination, constipation, abdominal pain and/or discomfort, loss of appetite and unexplained weight loss or weight gain. The treatment for peritoneal cancer basically depends on the stage of the disease. There are three treatment modalities for peritoneal cancer and they include surgical resection of the tumor, chemotherapy and radiation therapy.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...