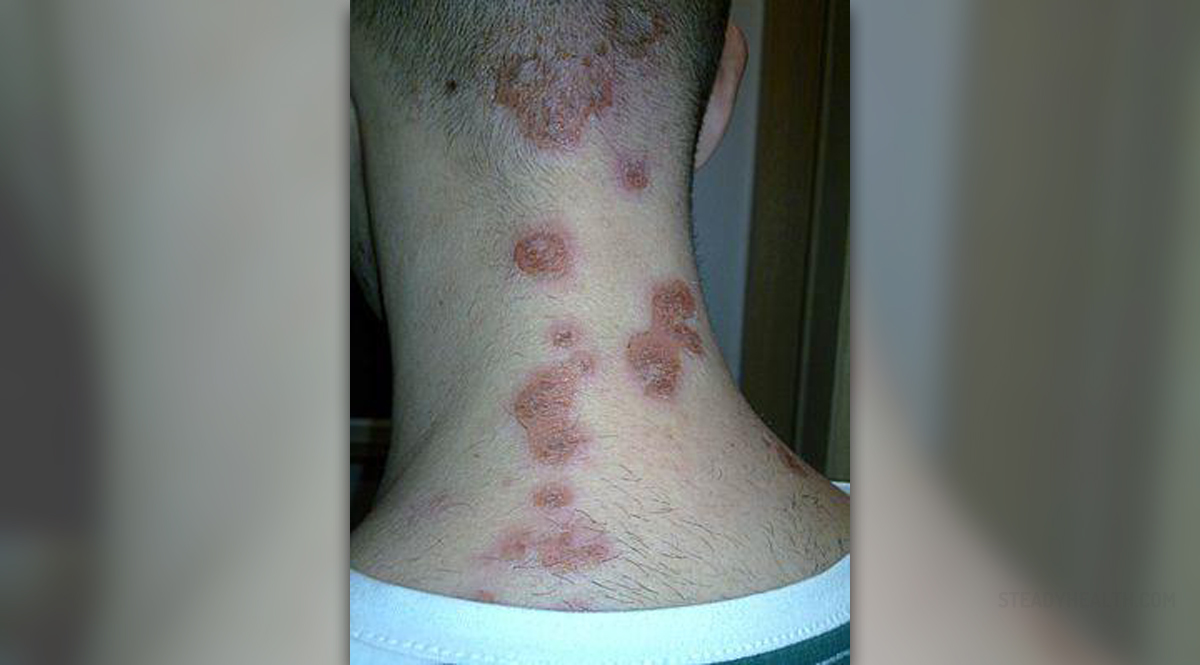
Impetigo represents a skin condition that develops after penetration of certain bacteria into the skin through cuts or insect bites. Impetigo may also develop in people whose skin is practically intact, having no cuts or cracks present. This is a highly contagious infection most commonly affecting infants and children, although it is reported in adults as well.
In many cases the condition develops in a form of red sores distributed on the face, around the nose or mouth.
The condition is usually not so severe and may clear spontaneously within several weeks. On the other hand, impetigo may initiate some more complex complications and this is the reason why patients may need to be prescribed antibiotics.
Types of Impetigo
Impetigo may develop in two forms, as bullous impetigo and non-bullous impetigo. The first form of the disease is actually a toxin-mediated erythroderma accompanied by excessive loss of skin. Non-bullous impetigo is also known as impetigo contagiosa. This is a superficial infection predominantly affecting children. This form of the disease is contagious and develops in preexisting wounds.
Ecthyma is a bit deeper infection, an ulcerated form of the disease and a complication of impetigo accompanied by lymphadenitis.
Impetigo Treatment Options
The very treatment for the condition can accelerate healing of skin sores and improve the skin's appearance. Treatment is also an excellent means of prevention. Namely, it keeps the infection localized not allowing it to spread and affect larger portions of the skin. What treatment option is going to be applied basically depends on several factors. The most important ones are the type of impetigo and the severity of the condition.
Hygienic measures are crucial and sometime the only approach doctors recommend. This treatment is used in minor cases of impetigo. With adequate hygienic measures skin sores soon withdraw.
More complex cases require topical antibiotics. These are in a form of creams or ointments. Mupirocin and retapamulin are applied after one removes scabs from the affected skin. This allows better penetration of the antibiotic.
Finally, oral antibiotics are prescribed in severe cases of impetigo. They are treatment of choice in individuals suffering from widespread impetigo, ecthyma and those with impetigo contagiosa. The doctor choses the most convenient antibiotic and pays close attention to allergies the patient is suffering from. It is essential to finish the entire course of antibiotics even if the skin lesions have completely healed. With adequate treatment infection can be completely cured and there will be no disease recurrence.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...