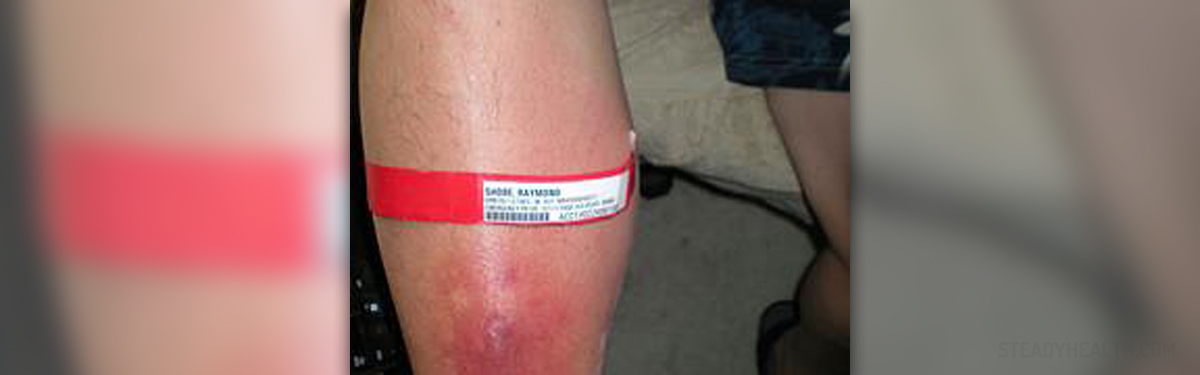
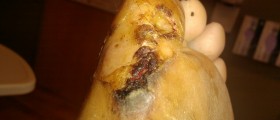
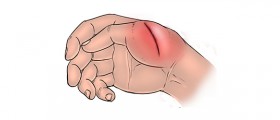
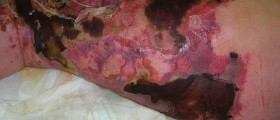
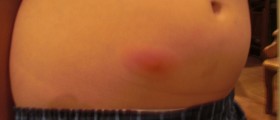
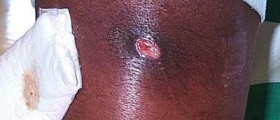
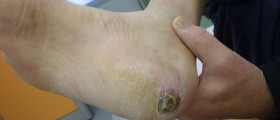
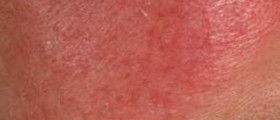
Cellulitis is a skin infection, to be more precise, infection of the deep layer of the skin together with infection of fat tissue and tissues located just beneath the skin. The infection develops and spreads rapidly. The affected skin is swollen, red, hot and tender to touch.
More about Cellulitis
In majority of cases cellulitis occurs in the legs, although this infection may affect other body parts as well. In severe cases the infection may even spread to regional lymph nodes and into the bloodstream. Because of these potential complications and several more it is essential to treat cellulitis as soon as it has been diagnosed i.e. as soon as the symptoms develop.
Most common symptoms and signs of cellulitis include redness, swelling and tenderness of the affected skin. The area is painful and warm. The person also develops fever. The skin may be additionally covered with small red spots and in rare cases there are blister which can easily burst.
Prevention of Cellulitis
There are certain measures which can successfully prevent not only cellulitis but also other infections. This particularly refers to people who have wounds. Namely, wounds can be easily infected and infection may progress into cellulitis. In such case the wound is supposed to be washed with soap and water on daily bases. After proper cleaning the wound should be covered with an antibiotic cream or ointment.
Each and every individual is due to pay close attention to potential signs of infection such as redness of the skin around the wound, pain etc.
People who are suffering from certain conditions such as diabetes and illnesses that cause improper circulation must pay even more attention because they are prone to skin wounds and easily develop skin cracks and cuts which can be excellent sites for penetration of bacteria. Such patients are due to check their skin, especially their feet daily for any sign of injury. They are also supposed to moisturize their skin and keep it properly lubricated.Treatment for CellulitisCellulitis is a serious infection and requires prompt treatment with antibiotics. The treatment must be aggressive because only this way the bacteria responsible for the infection can be eradicated. Prescribed antibiotics are supposed to be taken for at least 14 days. Even though symptoms and signs of the infection may start to withdraw a few days after the onset of the treatment, it is essential to finish the entire course of antibiotics. Always follow doctor's orders and finish the entire therapy. Patients who do not respond to oral antibiotics are administered antibiotics intravenously.








Your thoughts on this
Loading...