Cirrhosis is a severe medical condition characterized by replacement of normal, healthy liver tissue with non-functional scars. It is actually the terminal stage of many different chronic liver diseases.
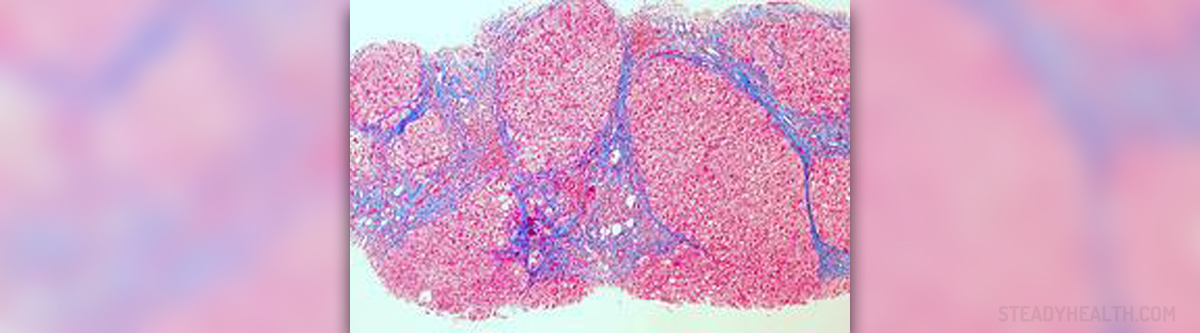
Histologically cirrhosis represents diffuse hepatic process associated with fibrosis and changes of normal liver architecture into abnormal and non-functional nodules. The condition may progress rapidly (within several weeks) or slowly (within several years).
Even though the liver possesses the ability to regenerate, in case of liver cirrhosis regeneration is not possible. Instead, the organ loses most of its functional cells which eventually results in decrease and finally loss of different liver functions. For instance, there is decreased hepatic synthetic function, decreased detoxification capability and portal hypertension.
Treatment for Cirrhosis
Even though doctors try to completely cure the diseases affecting the liver which may, in the long run, progress into cirrhosis, prevention of this debilitating condition, unfortunately, is not always possible.
Once the condition fully develops, there are different treatments that can be and are used. The goal of the treatment is to bring the symptoms patients have to face with under control and prevent some, if not all, potential complications. Patients suffering from liver cirrhosis may develop a variety of complications. Ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, portal hypertension and esophageal varices are only some of them.
Liver Cirrhosis - Dietary Changes
Many people suffering from cirrhosis are anorexic. The compression of the accumulated fluid inside the abdominal cavity may induce the feeling of fullness and reduce food intake. Diet for such patients must have optimal amount of calories and contain sufficient amount of proteins. Additional help is obtained from liquid and powdered nutritional supplements.
Liver Cirrhosis Adjunctive Therapies
Patients suffering from liver cirrhosis commonly suffer from zinc deficiency. This problem is managed with zinc sulfate that is taken on daily bases. This mineral may stimulate appetite and relieve muscle cramps.
Pruritus (itching) if not severe enough may be treated with antihistamines or topical ammonium lactate.
More complex manifestations of the disease such as esophageal varices, portal hypertension, hepatic encephalopathy etc. are treated in a hospital. Depending on the complication patients are either treated conservatively or they undergo some surgical procedures. For instance, hepatic encephalopathy is treated with certain drugs while esophageal bleeding requires surgical approach.
Life support is essential for patients with breathing difficulties and those who deal with inadequate blood circulation. Patients in coma also require life support.
Finally, the only way to cure patients is to perform liver transplantation.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...