
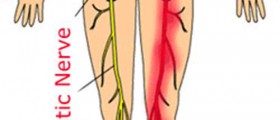
Cubital tunnel syndrome is a medical condition that leads to a variety of problems all of which develop as a consequence of pressure on the ulnar nerve. The ulnar nerve is one of the main nerves innervating certain muscles of the upper extremity. Its compassion is associated with different neurological symptoms and signs such as elbow pain, weakness/clumsiness of the hand and tingling sensation or numbness of the ring and small finger. Anatomical peculiarities of the elbow and the very location of the ulnar nerve in this area are to blamed for the occurrence of cubital tunnel syndrome.
Cubital tunnel syndrome is estimated to be the second most common compressive neuropathy, following carpal tunnel syndrome. The condition is 3-8 times more frequent among men.
What Causes Cubital Tunnel Syndrome?
The ulnar nerve starts in the spinal cord and eventually reaches certain muscle of the forearm and hand. It also innervates the skin on the pinkie side of the hand. On its way down the hand, the nerve passes across the back of the elbow, behind a protrusion (the medial epicondyle) on the inner side of the upper arm bone. In case an individual hits the elbow at this spot, he/she will experience a brief tingling sensation.
Bending of the elbow may induce stretching of the nerve and push it against the bony bump. Prolonged bending position of the elbow may aggravate stretching of the ulnar nerve and is responsible for its irritation. This irritation should be identified and treated on time. Only this way potential complications may be efficiency avoided.
The irritation of the nerve is also possible in case of subluxation of the ulnar nerve over the medial epicondyle, cubital valgus, bony spurs and hypertrophied synovium. The condition is also associated with tumors, ganglia and other causes of direct nerve compression.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Treatment
Initial care includes over-the-counter NSAIDs such as Aspirin, ibuprofen etc. Vitamin B6 supplements may be beneficial as well. Elbow bending during healing can be prevented with splints or braces. Finally, patients should modify their posture and avoid holding the elbow bent for a long period of time.
In case the mentioned has not helped, one should consult a doctor. A health care professional may recommend a custom pad or support (prescription splint) that keeps the elbow from bending during sleep. Furthermore, he/she can prescribe stronger NSAIDs and suggest hand therapy.
Surgery is only recommended in case there is no improvement of symptoms in spite of adequate conservative treatments. The goal of the surgery is to provide with more space for the nerve and tendons. It is also important to reduce compression of the nerve. The surgeon can move the nerve in front of the bump and this way prevent its stretching during elbow bending or he/ she removes the bump, allowing the ulnar nerve to move and glide back and forth during elbow bending. The first procedure is medically known as an ulnar nerve transposition while the second one is called a medial epicondylectomy.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...